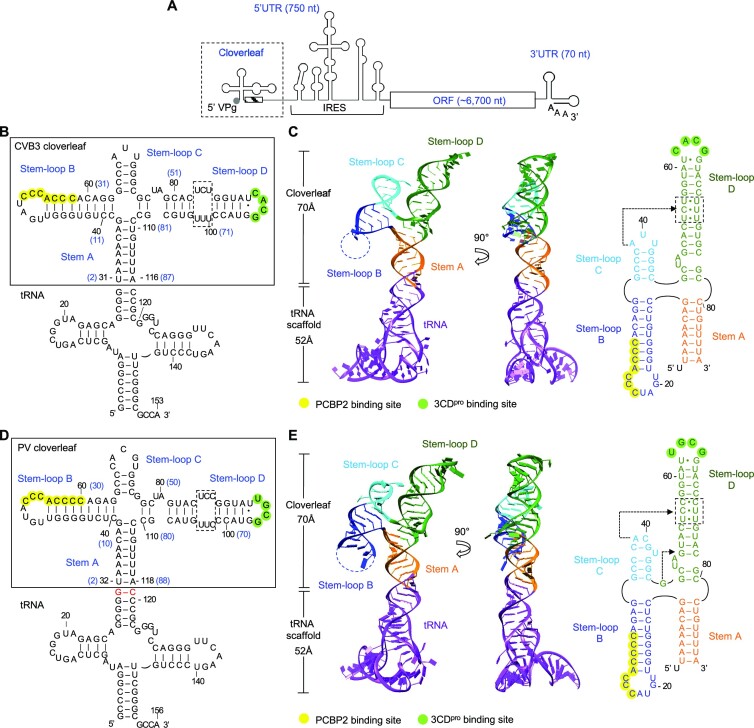
Figure 1.
Enterovirus cloverleaf RNA forms an H-type four-way junction. (A) Schematic representation of an enterovirus genome. The genome contains one open reading frame (ORF), flanked by a highly structured 5′ untranslated region (UTR) and a 3′ UTR with a poly(A) tail. The 5′ UTR contains the cloverleaf and internal ribosome entry site (IRES) structures and is covalently linked to VPg (viral protein genome-linked). The cloverleaf structure is located at the 5′ terminus of the 5′ UTR immediately followed by the 3′ poly-rC region (hatched box). (B) Design of tRNA-fused coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) cloverleaf. CVB3 cloverleaf (nucleotides 2–87) is inserted into the anticodon loop of human tRNALys scaffold sequence to create tRNA-CLCVB3. The nucleotide numbers in cloverleaf are also shown on the secondary structure in parenthesis in blue. Cloverleaf consists of stem A and stem–loops B, C and D. The PCBP2 binding site in stem–loop B is colored in yellow, and the 3CDpro binding site is colored in green. The pyrimidine mismatch region in stem–loop D is boxed. (C) Crystal structure of CVB3 cloverleaf fused with a tRNA-scaffold. Cloverleaf RNA is colored by domain: stem A, orange; stem–loop B, blue; stem–loop C, cyan; and stem–loop D, green. The tRNA scaffold is colored purple. The missing nucleotides in stem–loop B are indicated by a dotted line. The secondary structure of CVB3 cloverleaf derived from the crystal structure is shown on the right. The PCBP2 binding site, the 3CDpro binding site and the pyrimidine mismatch region are highlighted as in (B). The nucleotides involved in the A•C-U base triple are indicated by an arrow. (D) Design of tRNA-fused poliovirus (PV) cloverleaf. The PV cloverleaf sequence (nucleotides 2–88) is inserted into the anticodon loop of human tRNALys. Additional G-C base pair was introduced between the tRNA scaffold and PV cloverleaf sequence to facilitate crystallization (colored in red). Functional regions in tRNA-CLPV are indicated as in (B). (E) Crystal structure of PV cloverleaf fused with a tRNA-scaffold. The tRNA-CLPV construct is colored by domain as in (C). The secondary structure derived from the crystal structure is shown on the right. PV cloverleaf has two base triples A•C-U and G•G-C, and their locations are indicated with arrows.