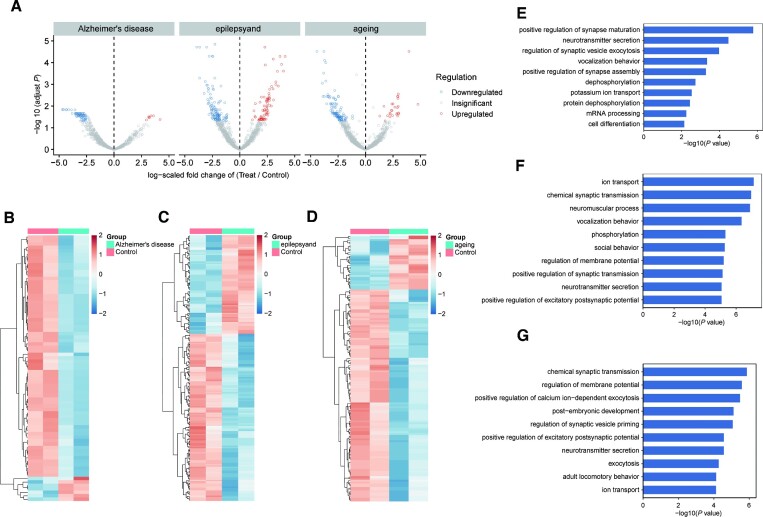
Figure 5.
Differential editing sites identified in three neurological diseases of mouse brain tissue. (A) Volcano plots showing A-to-I editing differentially between WT and treated models. Editing level significantly upregulated (red) or downregulated (blue) were identified in brain tissue. Editing sites detected in each sample of the control groups and the experimental groups were selected. Editing sites number, Alzheimer's disease: n = 1005, epilepsy: n = 1346; ageing: n = 1570; (B–D) heat map of the significant differential editing sites. (B) 77 differential editing sites in Alzheimer's disease, (C) 202 differential editing sites in epilepsy; (D) 148 differential editing sites in ageing were identified using the edgeR package (FDR < 0.05; log2(fold change) > 1); (E, F) GO analysis of enriched terms of genes with downregulated inosine abundance. GO enrichment analysis of genes with editing sites significantly downregulated or upregulated in (E) Alzheimer's disease, (F) epilepsy and (G) ageing. Significance of enrichment was determined by –log10(adjusted P value). The P value was provided by DAVID online tool and calculated with Fisher's exact test.