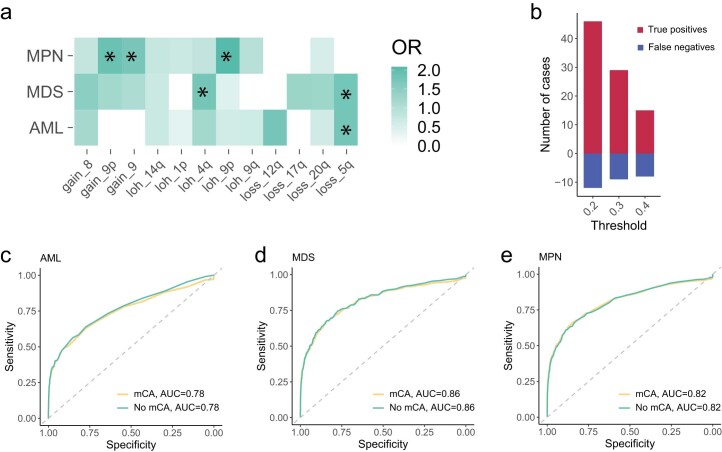
Extended Data Fig. 2. Impact of mosaic chromosomal abnormalities on MN prediction models.
(a) Associations between the risk for different types of MN and mosaic chromosomal alterations (mCA, * = Fisher’s test p < 10−5, see Supplementary Table 10 for details; OR = odds ratio). (b) Number of true pre-MN cases whose prediction changed by the inclusion of mCAs to the models. We calculated differences between 15-year MN-free survival probabilities of models including mCAs (with mCA) vs excluding mCAs (without mCA). We then tested three thresholds for the difference in MN probability between the two models. The lowest probability difference of 0.2 led to the correct identification of an additional ~45 pre-MN cases (true positives), at the expense of missing 12 such cases (false negatives). Higher difference thresholds still identified more true positives than false negatives. (c–e) Inclusion of mCA to our MN prediction models did not significantly improve model performance as assessed by area under curve (AUC) of recover operating curve for (c) AML, (d) MDS or (e) MPN. Dotted diagonal lines indicate AUC = 0.5.