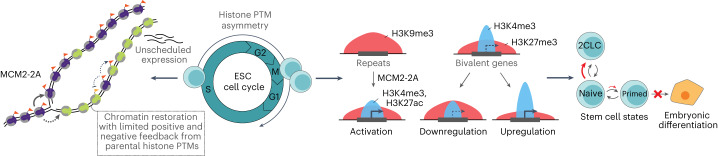
Fig. 7. Model illustrating how asymmetric histone segregation challenges epigenome fidelity and ESC functionality.
H3–H4 asymmetry in MCM2-2A cells creates a lagging strand largely devoid of parental histone PTMs, which affects the accuracy of chromatin restoration and creates a permissive environment for unscheduled expression in every cell cycle. This broadly alters the histone PTM epigenome with both local and global changes in repressive modifications. MCM2-2A cells show loss of H3K9me3-based repeat repression, misregulation of H3K27me3 and bivalent genes, and reduced ESC plasticity and embryonic differentiation. Naïve, naïve pluripotency; primed, lineage-primed states; new histones, green; parental histones, purple.