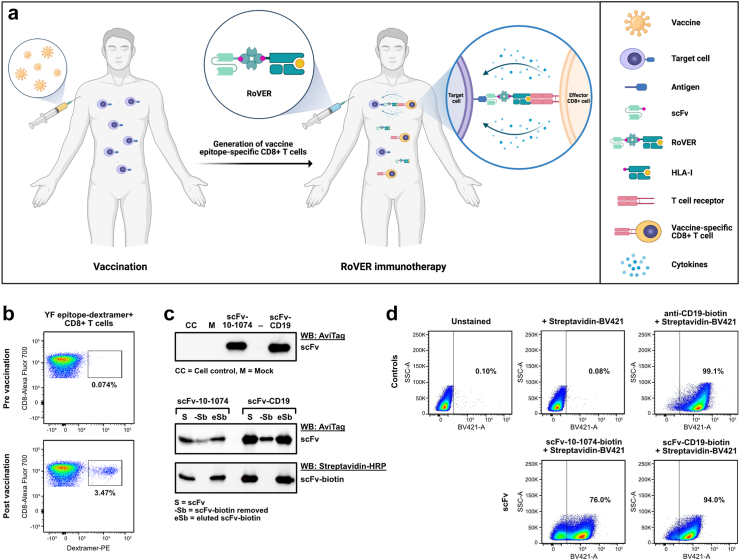
Fig. 1.
Functional assessment of RoVER components. a) Graphics of the RoVER technology. A vaccine induces potent vaccine epitope-specific CD8+ T cell responses which are redirected towards a cellular target of choice by administration of the bispecific RoVER. Graphics created with BioRender.com. b) Representative flow cytometry plots from dextramer staining of donor peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) pre and post YF-17D vaccination (21 ± 3 days) showing vaccine-induced epitope-specific CD8+ T cell responses. c) Western blots with anti-AviTag or Streptavidin-HRP showing successful expression and biotinylation of scFv-10-1074 and scFv-CD19 proteins from transient transfection of mammalian cells with pcDNA3.1 (+) expression plasmids encoding the scFvs. d) Functional assessment of the target cell binding capacity of scFv-10-1074 and scFv-CD19 proteins by flow cytometry analyses using Raji-Env cells with stable expression of GFP, CD19 and HIV-1 envelope using BV421-conjugated streptavidin. Controls included unstained Raji-Env cells or cells stained with a biotin-conjugated anti-CD19 antibody and/or streptavidin-BV421.