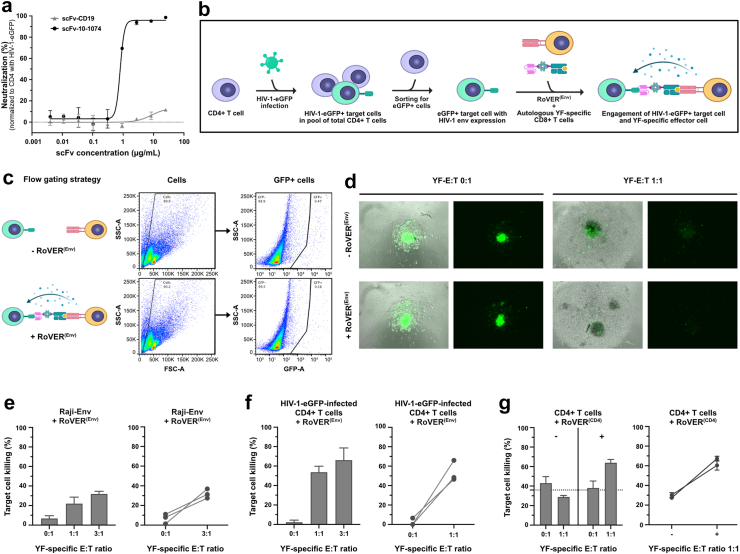
Fig. 5.
Specific killing of HIV-1 envelope-expressing target cells using the RoVER technology. a) Neutralization data for scFv-10-1074 and scFv-CD19 showing specific binding of scFv-10-1074 to HIV-1 envelope (n = 3). Normalized to HIV-1-eGFP-infected CD4+ T cell control without scFv. b) Graphics of the workflow for killing of HIV-1-infected CD4+ target cells by autologous CD8+ T cells using RoVER(Env) (Created with BioRender.com). c) Flow cytometry gating strategy for HIV-1 target cell killing assays. d) Fluorescence microscopy images of killing assay wells for the autologous setup with HIV-1-eGFP-infected CD4+ cells at different YF-E:T ratios with or without exposure to RoVER(Env). HIV-1-eGFP-infected target cells are identified by eGFP expression (green). RoVER(Env)-mediated killing of e) Raji-Env cells expressing HIV-1 envelope and GFP (n = 3) or f) autologous CD4+ T cells obtained from YF-17D vaccinated study participants and ex vivo infected with HIV-1-eGFP (n = 3). g) RoVER(CD4)-mediated killing of autologous CD4+ T cells (n = 2). All HIV-1 killing assay data shows the disappearance of HIV-1 envelope-expressing target cells (GFP+) normalized to the number of target cells in control wells without exposure to RoVER(Env). CD4 killing data shows the percentage of dead (Live/Dead stain) target cells (Celltrace+). The killing data are mean ± SEM for all donors (bar graph) or for individual donors (XY-graph) at indicated YF-E:T ratios. The dotted line is calculated based on the bars on the left side of each diagram and indicates the mean background target cell death.