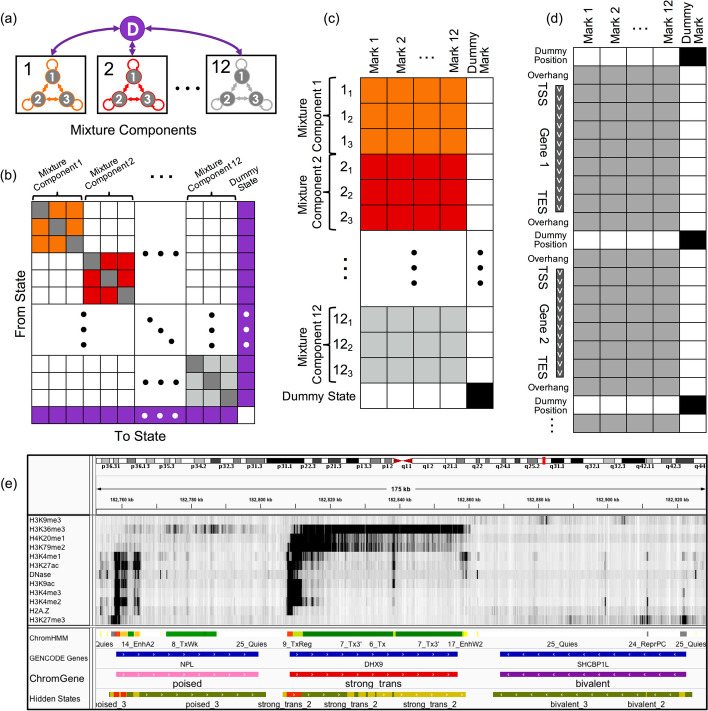
Fig. 1.
Overview of ChromGene. a ChromGene Model. Each gene is assumed to be generated by one of M = 12 mixture components, each of which is defined by S = 3 hidden states. Transitions within mixture components are allowed, but transitions between mixture components are only allowed by transitioning through the “dummy state” (purple), which only occurs between genes. b Transition matrix. The states within a component have learned probabilities of transition between them (colored and gray “self-transition” cells), but transitions between states in different components are disallowed (white). All states within components are allowed to transition to the dummy state (purple, right column), and the dummy state can transition to any state within any component (purple, bottom row). c Emission matrix. Each state has a separate emission probability for each input mark (colored and gray cells), corresponding to Bernoulli random variable parameters, and the probability of a set of observed marks is modeled using a product of those Bernoulli random variables. States within mixture components are enforced to never emit the “dummy mark” (white, right column), while the dummy state (bottom row) is enforced to never emit input marks (white) and always emit the dummy mark (black). d Data matrix. Input data across all genes and flanking regions is concatenated, with a single observation of “dummy position” between genes. Input data may be emitted within gene body or flanking regions (gray), but not at dummy positions (white cells). The dummy mark (right column) is only emitted at dummy positions (black cells). e IGV browser track [26] view using 12 input marks, “ChromHMM” annotations [27], “GENCODE Gene” track, mixture components (“ChromGene”), and components’ hidden states (“Hidden States”; red: state 1, yellow: state 2, green: state 3). Importantly, components’ hidden states are not comparable across different components and are not used in any analysis in this study