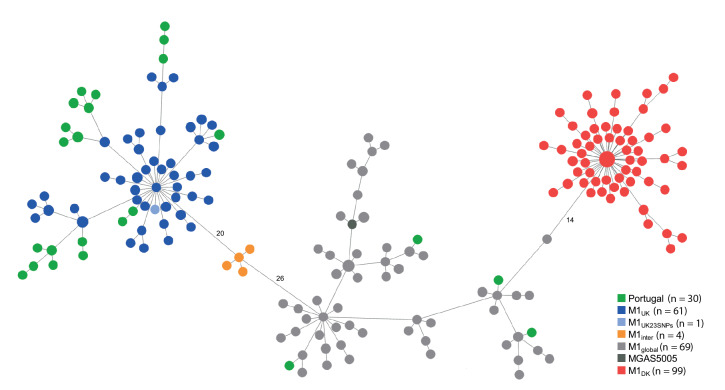
Figure 2.
Minimum spanning tree of paediatric invasive emm1 group A Streptococcus isolates, Portugal, 1 September 2022–31 May 2023 (n = 30), and of emm1 isolates from United Kingdom, 2009–2016 (n = 135) and Denmark, 2022–2023 (n = 99)
cgMLST: core genome multilocus sequence typing; UK: United Kingdom.
The tree was generated with the cgMLST profiles of paediatric invasive emm1 isolates recovered in Portugal, 1 September 2022–31 May 2023 (n = 30; green), non-invasive isolates (n = 135) recovered in London, UK [4] carrying 27 (dark blue), 23 (light blue), 13 (orange) or 0 (light grey) of 27 SNPs characteristic of the M1UK sublineage, invasive and non-invasive isolates from Denmark (n = 99) [5] carrying the 15 SNPs characteristic of the M1DK sublineage (red), and the M1 reference strain MGAS5005 (dark grey). The list of genomes used is available in Supplementary Tables S1 and S2. The size of each node is proportional to the number of isolates with that particular cgMLST profile on a logarithmic scale. Link distances separating the previously identified sublineages are labelled as the number of allelic differences between nodes (from a total of 1,249 compared loci). All isolates from Portugal carrying ≥ 26 M1UK SNPs (n = 26, found in Supplementary Table S1) grouped with the M1UK isolates, while the four isolates without M1UK SNPs grouped with M1global isolates. Link distances in the minimum spanning tree vary from 1 to 16 allelic differences between M1UK nodes, from 2 to 4 allelic differences between M1inter nodes, from 1 to 6 allelic differences between M1DK nodes, and from 1 to 40 allelic differences between M1global nodes. A maximum likelihood tree of the same isolates can be found in Supplementary Figure S1. Detailed high-throughput sequencing and data analysis methods can be found in the Supplementary materials.