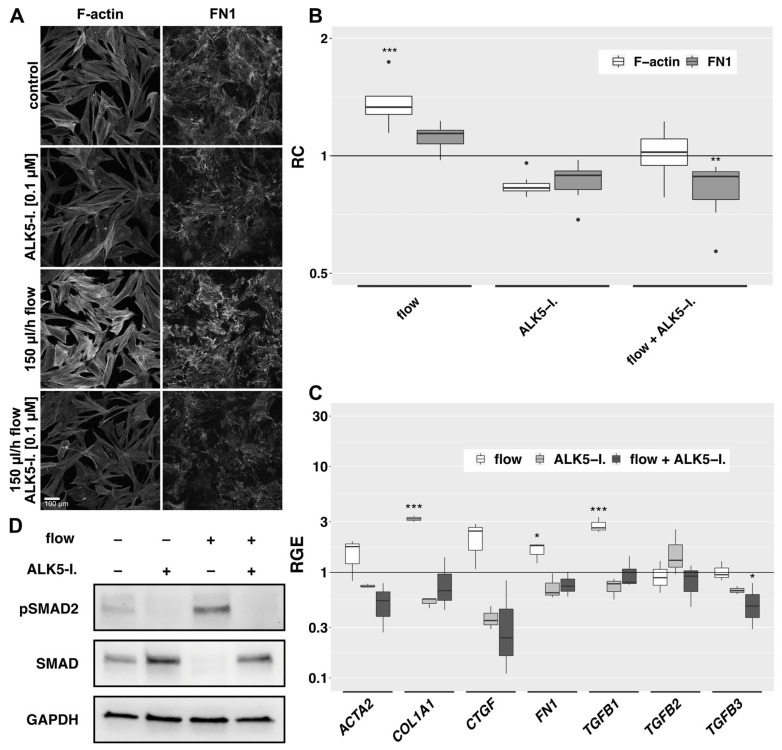
Figure 7.
Effects of ALK5-inhibition on the flow-induced changes. (A): Effect of ALK5-I. (0.1 µM) on flow-exposed HTF in the 2D model. Cells were preincubated in µ-slides for 24 h in 0.2% FBS medium, then for additional two days incubated either in static or flow conditions in the absence or presence of an ALK5-I. F-actin and FN1 were detected by IF. Image acquisition and representation settings are identical for all conditions. The result is representative of seven independent experiments. (B): The relative change in the mean signal intensity of F-actin and FN1 in the confocal images of the seven independent experiments as displayed in Figure 7A is shown, with a region of interest automatically defined by ImageJ. Image acquisition and representation settings are identical for all conditions. Asterisks indicate levels of significance in Dunnett’s t-test (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001). (C): Relative gene expression of fibrosis-associated genes in the 3D model under flow (666 µL/h), static conditions with ALK5-I. and flow conditions with ALK5-I. (0.1 µM, respectively) compared to static controls (72 h, n = 4). Asterisks indicate levels of significance according to Dunnett’s t-test (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001). (D): Western blot analysis of protein levels in whole cell lysates of the 3D model under static conditions or flow (180 µL/h) in the absence or presence of an ALK5-inhibitor (0.1 µM, 72 h, n = 3).