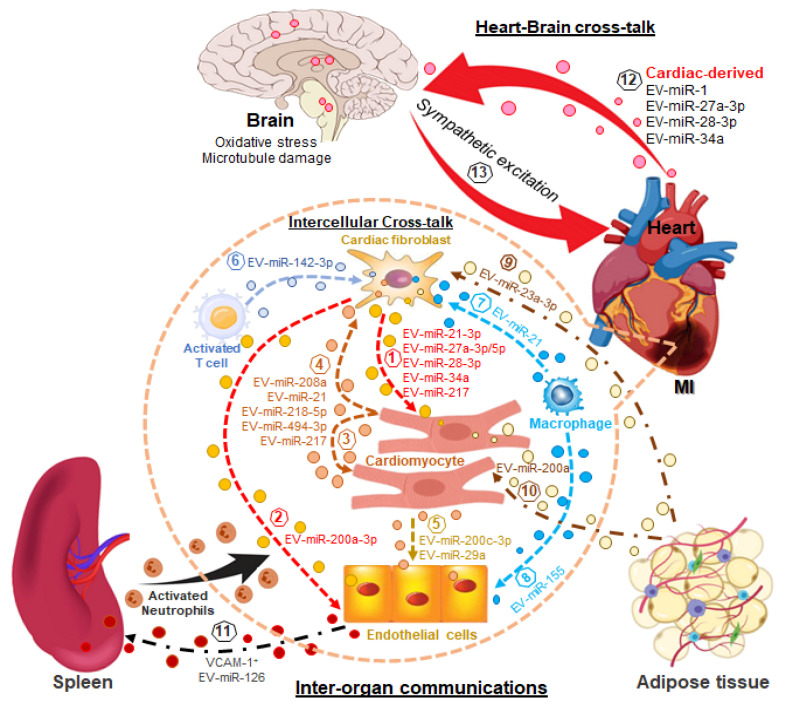
Figure 2.
EV miRNAs in the pathogenesis of heart failure via intercellular and inter-organ communication. miRNA-enriched EVs mediate intercellular communications: EVs from cardiac fibroblasts contribute to cardiac hypertrophy (1) and the impairment of angiogenic capacity (2); EVs derived from cardiomyocytes contribute to cardiac hypertrophy (3), fibrosis (4), and the impairment of endothelial proliferation, migration, and tube formation (5); EVs secreted by activated cardiac T cells (6) and macrophages (7) mediate cardiac fibrosis, and the inhibition of angiogenesis (8); miRNA-enriched EVs mediate inter-organ communications between adipose tissue (adipocytes) and cardiomyocytes and fibroblasts leading to fibrosis (9) and hypertrophy (10); heart (cardiac endothelial cells) and spleen (neutrophils) recruiting activated neutrophils to the ischemic region following MI increasing inflammation and promoting myocardial injury (11); cardiac derived cells communicate with neurons in the brain increasing oxidative stress and/or microtubule damage (12) eliciting sympathetic excitation which negatively regulates cardiac function in the setting of heart failure (13).