FIGURE 2.
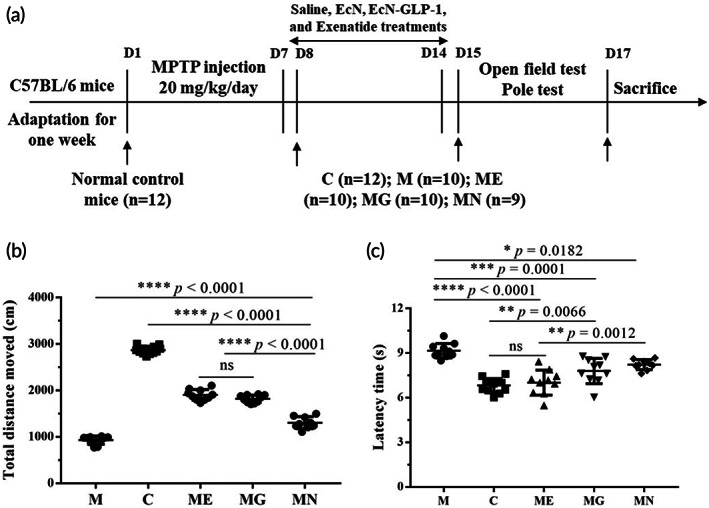
EcN‐GLP‐1 ameliorated the motor deficits in 1‐methyl‐4‐phenyl‐1, 2, 3, 6‐tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)‐induced Parkinson's disease (PD) mice. (a) The experimental scheme of this study. (b) EcN‐GLP‐1 increased the total moving distance of PD mice (open‐field test). (c) EcN‐GLP‐1 improved the bradykinesia of PD mice (pole test). C group, the normal control mice were treated with sterilized saline (n = 12); M group, the MPTP‐induced PD mice were treated with sterilized saline (n = 10); ME group, the MPTP‐induced PD mice that were orally taken EcN‐GLP‐1 (n = 10); MG group, the MPTP‐induced PD model mice were intraperitoneally injected with exenatide (n = 10); MN group, the MPTP‐induced PD mice were given EcN (n = 9). Data were presented as means ± SD. Tukey's multiple comparisons test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ns indicates no significant difference (p > 0.05)
