FIGURE 3.
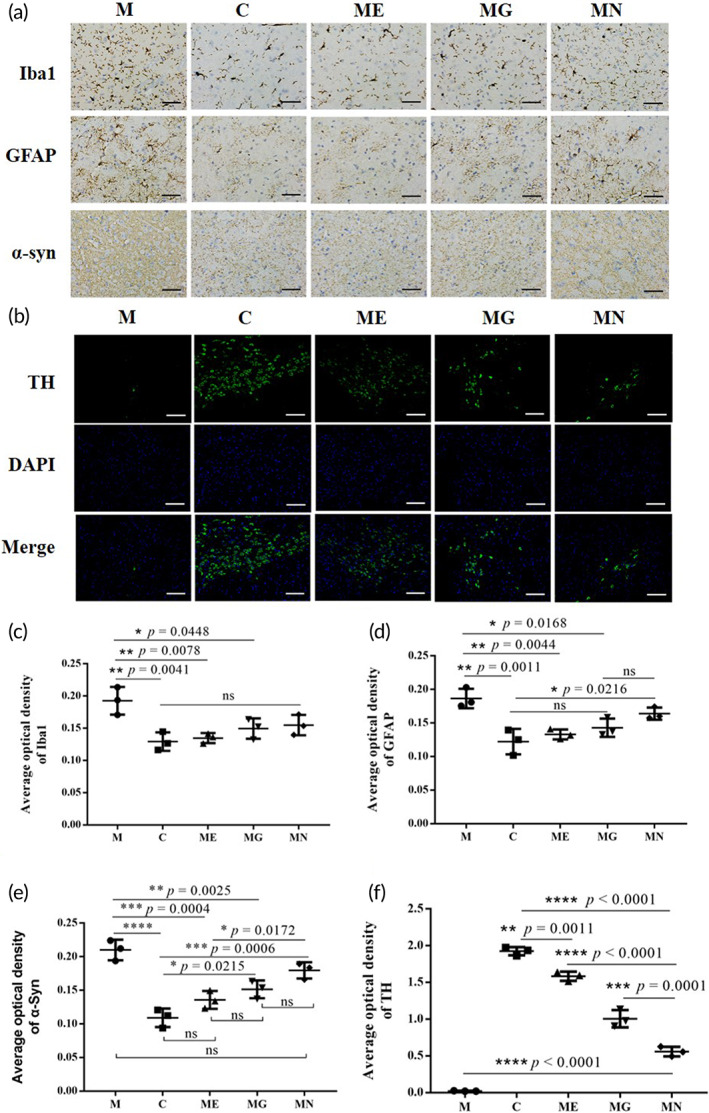
EcN‐GLP‐1 improved the neuropathologic damages in 1‐methyl‐4‐phenyl‐1, 2, 3, 6‐tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)‐induced Parkinson's disease (PD) mice. (a) EcN‐GLP‐1 inhibited the microglia activation (Iba1), astrocyte activation (GFAP), and reduced the synaptic dysfunction (α‐syn) in the substantia nigra of PD mice. Representative results of immunohistochemical analysis (IHC) of the Iba1‐positive microglia, GFAP‐positive astrocytes, and the expression of α‐syn. Magnification ×400, Scale bar = 50 μm. (b) EcN‐GLP‐1 alleviated the reduction of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)‐positive dopaminergic neuron numbers in the substantia nigra of PD mice. Representative results of immunofluorescence analysis (IF) of the TH‐positive cell numbers. Magnification ×200, scale bar = 100 μm. Quantification analysis of the content of Iba1 (c), GFAP (d), α‐Syn (e), and TH (f), which were related to the results of IHC and IF. C, The normal control group; M, the MPTP‐induced PD model group; ME, the EcN‐GLP‐1 treatment group; MG, the exenatide treatment group; MN, the EcN treatment group. Three mice of each group were randomly selected for analyzed, and data were presented as means ± SD. The significance of data was performed by Tukey's multiple Comparisons test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ns indicates no significant difference (p > 0.05)
