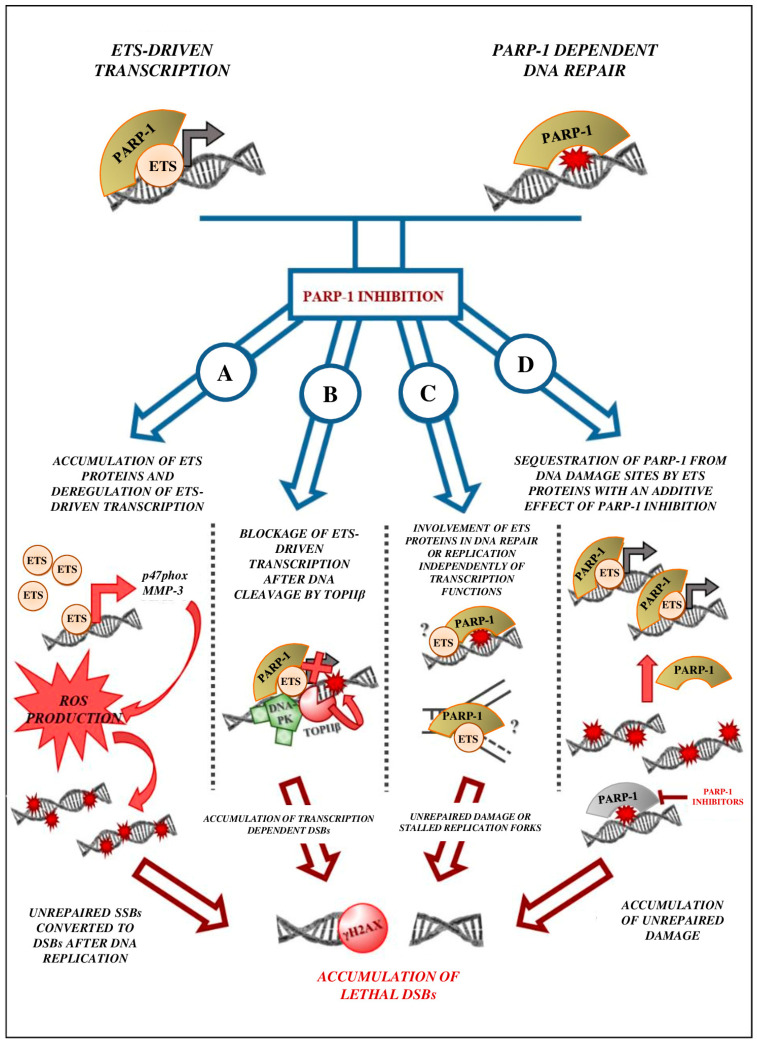
Figure 2.
Different hypotheses of ETS-driven DSB formation upon PARP-1 inhibition. (A) Ets-1 model: PARP-1 inhibition causes an accumulation of Ets-1 and an increase in its transcriptional activity. This provokes the production of ROS and inhibition of DNA repair, and therefore unrepaired SSBs are converted into DSBs after replication. (B) Erg model: PARP-1 inhibition blocks ETS-driven transcription after cleavage of DNA by topoisomerase IIβ. (C) Non-transcriptional (Myc) model: ETS factors have a non-transcriptional function in DNA damage during DNA replication; PARP-1 inhibition leads to defects in this process. (D) Sequestration model: ETS proteins sequestrate PARP-1 from DNA damage sites, decreasing DNA repair efficiency even more if PARP-1 is inhibited. All these models lead to an accumulation of lethal DSBs in cancer cells.