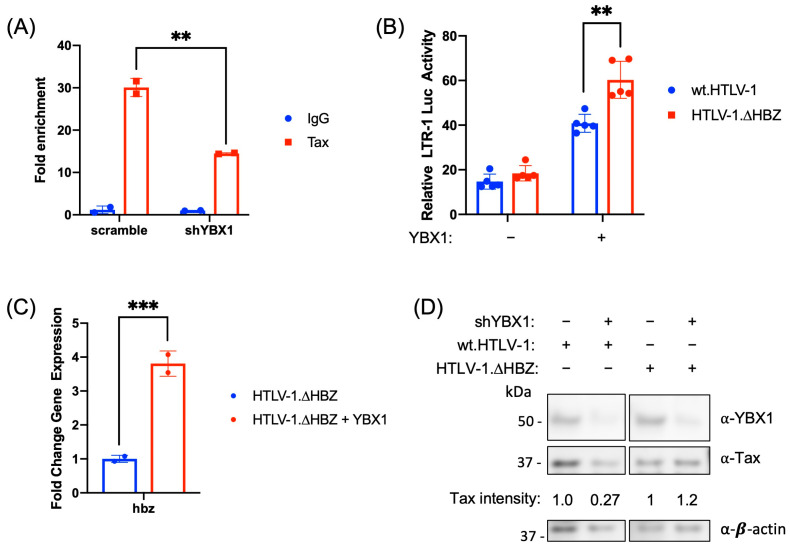
Figure 7.
YBX1 enhances Tax binding, and HBZ represses YBX1 transcriptional activation. (A) SLB-1 cells were transduced with lentiviral vectors expressing shRNA directed against YBX1. After a brief puromycin selection, ChIP assays were performed on cross-linked chromatin using either IgG or Tax antibodies. Retained DNA was amplified using 5′ LTR-specific primers and qPCR. Fold enrichment was calculated relative to the IgG sample. Each ChIP experiment was repeated twice in duplicate. (B) HEK293T cells were co-transfected with pcDNA3.1(+) empty, YBX1, wt.HTLV-1 proviral clone, a HTLV-1 proviral clone that lacks HBZ protein (HTLV-1.∆HBZ), HTLV-1 LTR-firefly luciferase, and tk-renilla luciferase (internal control) constructs, as indicated. At 48 h post-transfection, cells were collected for luciferase assays to measure relative LTR transactivation. The empty vector was set at 1. (C) Total hbz mRNA levels from HTLV-1.∆HBZ cells in (B) were determined using the ΔΔCt method, normalized to relative gapdh levels. HTLV-1.∆HBZ provirus alone was set at 1. (D) HEK293T scramble and shYBX1 cells were co-transfected with wt.HTLV-1 or HTLV-1.∆HBZ proviral clones, as indicated. After 48 h, total cell lysates were examined by immunoblot analysis using antibodies to YBX1, Tax, and β-actin. Tax protein intensity relative to β-actin in each scramble condition was set at 1. Graphs represent data generated from duplicate samples (5 samples for B), and error bars represent the standard deviation (SD). The data are representative of at least three experimental repeats. Statistical significance was determined using Student’s t-test: ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001.