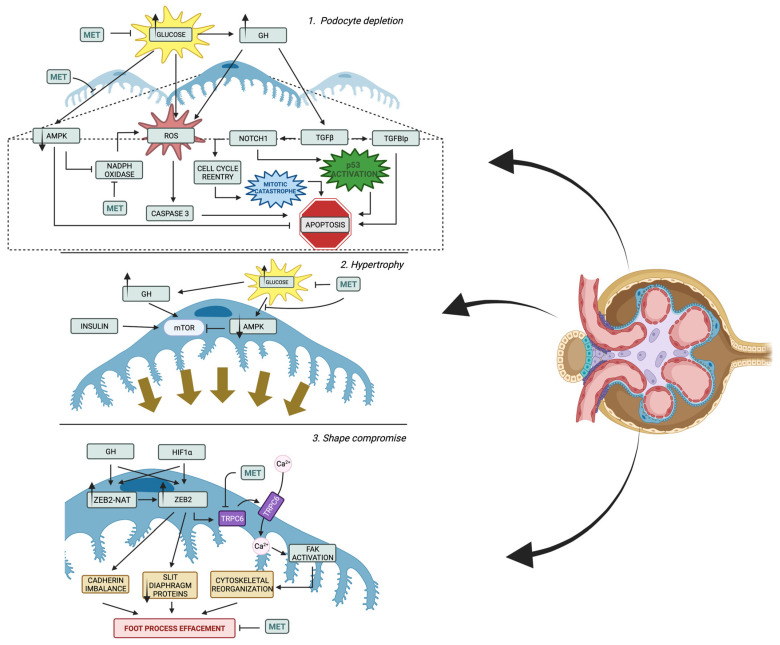
Figure 2.
Molecular pathways involved in podocyte alterations in DKD. 1. Apoptosis of podocytes may be the result of high glucose itself by stimulating reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, but the disrupted inhibiting pathway, including Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK), is also important for its overproduction and, consequentially, caspase 3 stimulation. Podocyte loss can occur also through apoptosis triggered by growth hormone (GH) stimulation. GH induces ROS buildup and higher expression of transforming growth factor-beta (TGFβ). TGFβ leads to the expression of Transforming Growth Factor-Beta-Induced Protein (TGFBIp), which promotes apoptosis. Notch1 activation by TGFβ induces podocyte cell death by activating p53 and Cdk1a. Additionally, podocytes in DKD undergo transition from a dormant state to cell-cycle re-entry, but are unable to complete cytokinesis, resulting in “mitotic catastrophe” and apoptosis. Metformin (MET) does not only influence podocytes’ apoptosis by lowering blood sugar level, but it also activates AMPK and decreases ROS production by inhibiting NADPH oxidase function. 2. Hypertrophy of podocytes is orchestrated by Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR), which might be induced by many factors. AMPK decrease seen in DKD progression is also important, since it is an inhibitor of mTOR and its level normalization may reduce hypertrophy in mTOR-independent manner. Metformin inhibits podocytal hypertrophy by decreasing glycemia and activation of AMPK described in detail below. 3. Podocytes undergo early adaptations that compromise their shape, leading to foot process effacement and slit diaphragm modulations. GH and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF1α) induce the expression of zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2 (ZEB2) and its natural antisense transcript (ZEB2-NAT), promoting ZEB2 translation. ZEB2 alters cadherin expression and decreases expression of slim diaphragm proteins, leading to shape compromise. In hypoxic conditions, the HIF1α/ZEB2/TRPC6 axis is activated, leading to calcium influx, focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activation, and cytoskeletal rearrangements. Moreover, these processes might be slowed down by metformin therapy. Created with Biorender.com.