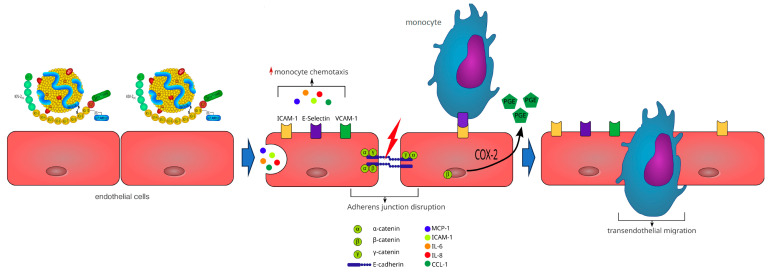
Figure 2.
Consequences of lipoprotein(a) interaction with vascular endothelium. Lp(a) crosses endothelial surfaces bound to oxidized phospholipids and binds to subendothelial structures. Once retained and oxidized, Lp(a) modifies the properties of endothelial cells that enhance expression of cell adhesion molecules and monocyte chemotaxis. Enhanced contraction and loss of contact of endothelial cells due to increased phosphorylation of myosin light chains and rearrangement of the actin cytoskeleton disrupts the integrity of the endothelial monolayer, leading to increased permeability and transendothelial migration of monocytes. Moreover, migration and adhesion of progenitor endothelial cells is impaired together with activation of endothelial cells apoptosis. K IV, kringle IV; LBS, lysine binding sites; oxPL, oxidized phospholipids; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule-1; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; PGE, prostaglandin E; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; IL-6, interleukin-6; IL-8, interleukin-8; CCL-1, CC chemokine ligand-1.