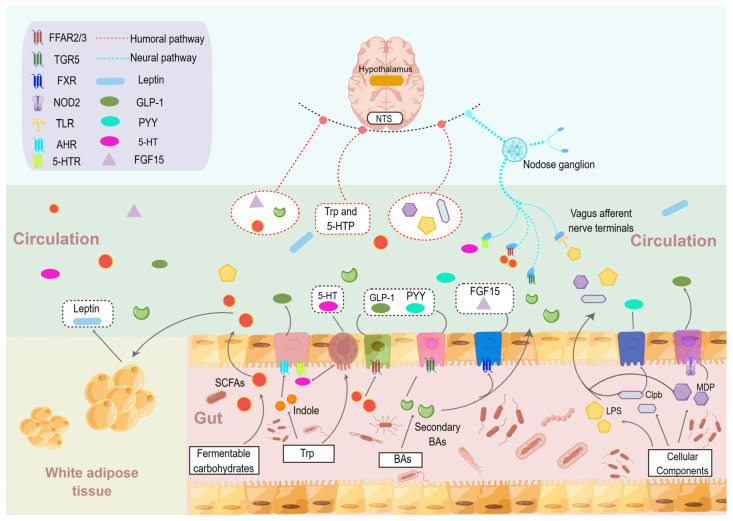
Figure 4.
Gut microbe-brain communication in the regulation of food intake. Gut microbes rely mainly on their functional metabolites and cellular components to mediate host food intake through humoral, enterodocrine, and neural signalling pathways. AHR, aromatic hydrocarbon receptor; Clpb, caseinolytic peptidase B; FGF15, fibroblast growth factors 15; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; FFAR2/3, free fatty acid receptor 2/3; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide-1; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MDP, muramyl dipeptide; NOD2, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 2; NTS, nucleus tractus solitarii; PYY, peptide YY; SCFAs, short-chain fattyacids; TGR5, takeda G-protein-coupled receptors 5; TLR, Toll-like receptor; Trp, tryptophan; 5-HT, 5-hydroxy tryptamine; 5-HPT, 5-hydroxytryptophan; 5-HTR, 5-HT receptor.