Figure 5.
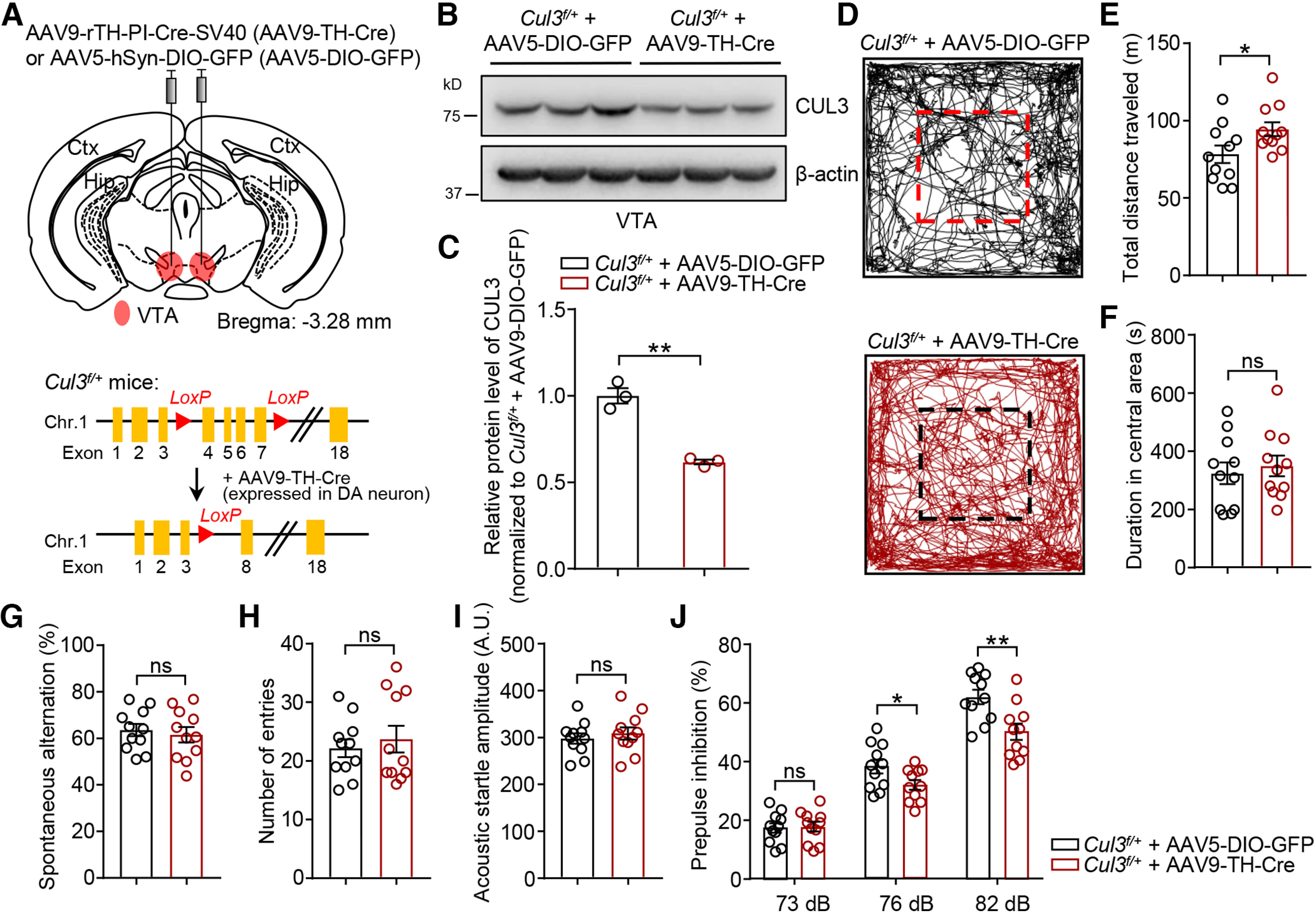
Increased locomotion and decreased sensorimotor gating induced by VTA DA neuron-specific Cul3 deficiency. A, Schematic diagram represents injection of AAV9-rTH-Cre (AAV9-TH-Cre) virus into VTA in P90 Cul3f/+ mouse (top) and experimental approach for Cre-dependent deletion of Cul3 in DA neurons (right). AAV5-hSyn-DIO-GFP (AAV5-DIO-GFP) virus was injected as control. B, Reduced CUL3 protein in VTA tissues from Cul3f/+ mice injected with AAV9-TH-Cre 4 weeks after injection. C, Quantification for data in B. n = 3 mice per group; p = 0.0087, t(2.368) = 8.152; unpaired t test. D, Representative traces of movement over 30 min in the arena for Cul3f/+ mice injected with indicated viruses. E, Increased distance traveled by AAV9-TH-Cre-injected Cul3f/+ mice in the open field compared with AAV5-DIO-GFP-injected mice. n = 11 mice, p = 0.0376, t(19.12) = 2.234; unpaired t test. F, Comparable time spent in the center in the open field. n = 11 mice, p = 0.6361, t(19.94) = 0.4805; unpaired t test. G, Similar spontaneous alternation in Cul3f/+ mice injected with AAV9-TH-Cre and those with AAV5-DIO-GFP in Y-maze test. n = 11 mice, p = 0.6340, t(19.24) = 0.4837; unpaired t test. H, Comparable total number of entries in Y-maze. n = 11 mice, p = 0.5809, t(17.32) = 0.5627; unpaired t test. I, Similar acoustic startle reflex. n = 11 mice, p = 0.5301, t(19.31) = 0.6394; unpaired t test. J, Impaired PPI at 76 and 82 dB in AAV9-TH-Cre-injected Cul3f/+ mice. n = 11 mice, p = 0.8599, t(19.99) = 0.1788 for 73 dB; p = 0.0451, t(18.17) = 2.152 for 76 dB; p = 0.0042, t(19.68) = 3.234 for 82 dB; unpaired t test. Data are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01.
