Figure 4. Antibodies 2C06 and 2C09 form a reproducible class.
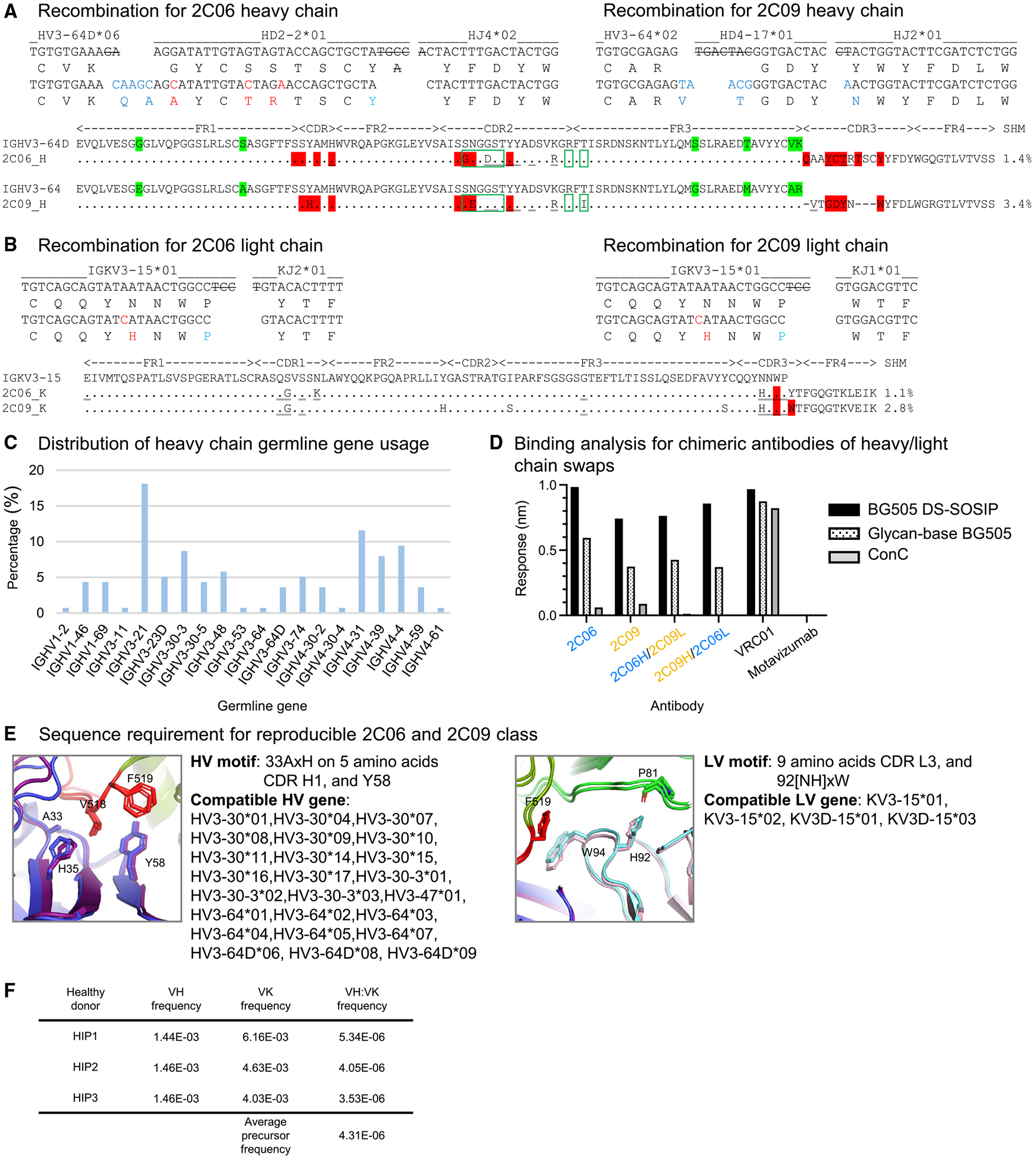
(A and B) Analysis of junction regions and sequence alignment of 2C06 and 2C09. Germline gene nucleotide and amino acid residues are shown in black. The somatic hypermutations are colored red. Nucleotides removed by exonuclease trimming are crossed out. Germline amino acid differences between IGHV3-64 and IGHV3-64D are labeled with green highlight. Fusion-peptide contacts (red highlight), glycan contacts (green rectangles), and additional trimer contacts (underlined) are highlighted.
(C) Heavy-chain germline gene usage of 138 antibodies isolated from donor N751.
(D) Binding analysis of chimeras swapping heavy and light chains between 2C06 and 2C09. Data were measured once.
(E) Sequence signatures of the reproducible 2C06 and 2C09 class for fusion-peptide binding. HV, heavy-chain variable; LV, light-chain variable. See also Table S6.
(F) Calculated precursor frequency of 2C06/2C09 antibody class for healthy donors HIP1–HIP3 (see STAR Methods).
