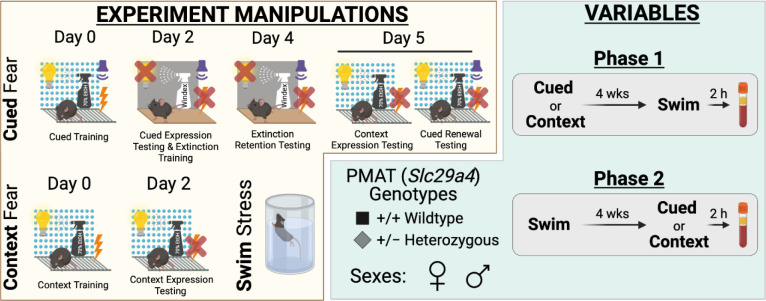
Figure 1.
Experimental manipulations and variables for study. Experimental manipulations involved cued fear conditioning, context fear conditioning, and swim stress (yellow compartment, left side). Cued fear conditioning (top, yellow compartment) involved cued fear training in Context A (visible light, grid floor, patterned background, ethanol scent) on Day 0, followed by cued fear expression testing and cued extinction training on Day 2 in Context B (infrared light, smooth floor, no background, Windex scent). On Day 4, testing of extinction retention occurred in Context B, then Day 5 involved testing mice in Context A for context expression testing followed immediately by cued fear renewal testing Note that for Day 5, the graphic shows the different conditions for context expression testing (left; 10 min) and cued fear renewal testing (right; 5 min) for clarity, but that in practice these tests occurred within the same continuous 15 min testing session. Context fear conditioning (bottom left, yellow compartment) involved context fear training in Context A on Day 0, with testing occurring in Context A on Day 2. Swim stress involved a six min inescapable immersion in room temperature water (bottom right, yellow compartment). Variables involved plasma membrane monoamine transporter (PMAT, Slc29a4) genotype, sex, swim condition, and the timeline of stressor exposure (Phase 1 or 2) (green compartment, right side). Wildtype (+/+) or heterozygous (+/−) mice of both sexes were used (bottom left, green compartment). Phase 1 (top right, green compartment) involved exposing mice to either cued or context fear conditioning, followed 4 wks later by swim stress; 2 h after swim stress, blood was collected for serum corticosterone analyses. Phase 2 (bottom right, green compartment) had mice undergo swim stress, followed 4 wks later by either cued or context fear conditioning; 2 h after the last test (Day 5, cued; Day 2, context), blood was collected for serum corticosterone analyses.