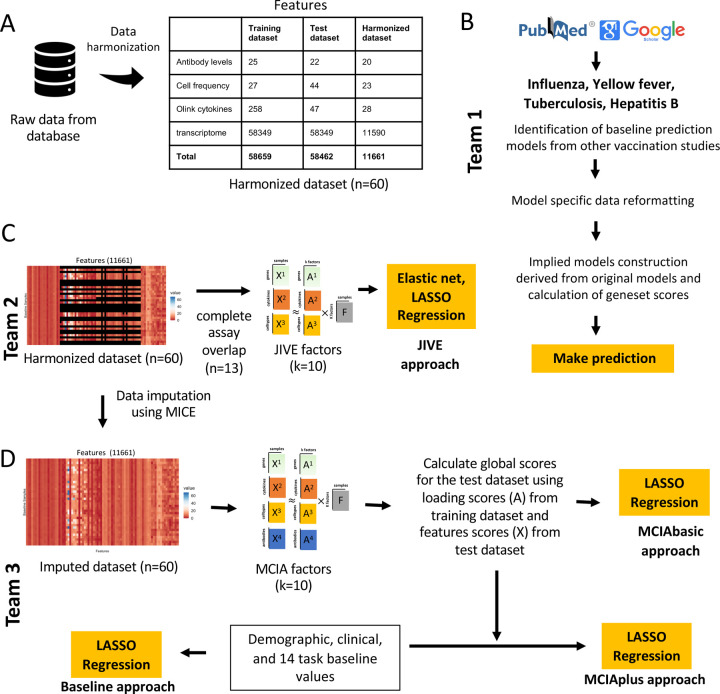
Figure 2. Data processing, computable matrices, and prediction model generation.
A) Generation of a harmonized dataset involved identifying shared features between the training and test datasets and filtering out low-information features. Literature-based models used raw data from the database and applied data formatting methods specified by existing models. In contrast, JIVE and MCIA utilized harmonized datasets for constructing their models. B) Flowchart illustrates the steps involved in identifying baseline prediction models from the literature, creating a derived model based on the original models’ specifications, and performing predictions as described by the authors. C) The JIVE approach involved creating a subset of the harmonized dataset by including only subjects with data for all four assays. The JIVE algorithm was then applied to calculate 10 factors, which were subsequently used for making predictions. JIVE employed five different regression models for prediction purposes. D) MCIA approach applied MICE imputation on the harmonized dataset and used this data for model construction. MCIA method was applied to the training dataset to construct 10 factors. Then, these 10 factors and feature scores from the test dataset were utilized to construct global scores for the test dataset. LASSO regression was applied to make predictions. MCIAplus model was constructed by including additional features (demographic, clinical features, and 14 task values) as factor scores, and it also utilized LASSO regression to make predictions. D) The MCIA approach utilized MICE imputation on the harmonized dataset for model construction. The MCIA method employed the imputed training dataset to construct 10 factors. These 10 factors, along with feature scores from the test dataset, were used to construct global scores for the test dataset. LASSO regression was applied to make predictions. Additionally, the MCIAplus model incorporated additional features such as demographic, clinical features, and 14 task values as factor scores. Finally, LASSO regression was employed for making predictions.