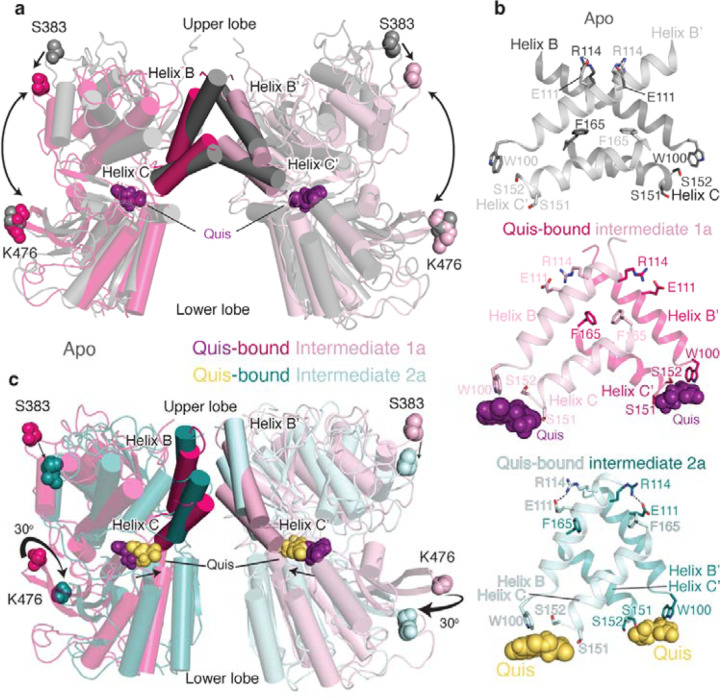
Fig 2: Structures of Quis-bound conformations of mGlu5 in nanodisc.
a) VFTs of Apo (grey, PDB: 6N52) and Quis-bound Intermediate 1a are overlayed. Upon Quis binding the upper lobe closes, as seen by the movement of S383, whereas not much change is seen in the lower lobe (comparing K476 between the structures). Also shown is the comparison of the B and C helices at the intersubunit interface in the Apo and Quis-bound Intermediate 1a state.
b) The intersubunit rearrangement upon Quis binding reorients the B and C helices leading to a reduction in the helix angle. Top: Apo, Middle: Quis-bound Intermediate 1a and Bottom: Quis-bound Intermediate 2a. Residue R114 interacts with E111 from the adjacent protomer in the Apo state and within the same protomer in the Quis-bound Intermediate 2a. The residue F165 is shown to illustrate the change in the position of the C helix. There is a downward movement of W100 towards Quis in Intermediates 1a and 2a. Due to the lower lobe rotation in Intermediate 2a, a further inward movement of Quis is seen.
c) Overlay of VFTs of Quis-bound Intermediate 1a and Quis-bound Intermediate 2a showing a small change in the upper lobe (movement of S383). The lower lobes twist 30° and move closer together as seen by comparing K476 between the structures. The B and C helices at the protomer-protomer interface in the Quis-bound Intermediate 2a state show an upward shift compared to the Quis-bound Intermediate 1a. This likely is the result of the inward movement of Quis (from purple to yellow) and the rearrangement of the lower lobe.