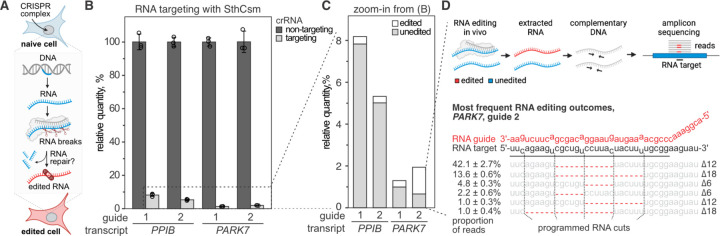
Fig. 1. Programmable deletions of RNA with RNA-guided type III-A CRISPR complexes.
A) Diagram of RNA editing in eukaryotic cells through sequence-specific RNA cleavage and RNA repair. B) Human cells (293T) were transfected with plasmids encoding for type III CRISPR complex of Streptococcus thermophilus (SthCsm), and RNA guides targeting PPIB or PARK7 messenger RNAs. Target transcripts were quantified with RT-qPCR, and the qPCR signal was normalized to ACTB and non-targeting guide RNA control using the ΔΔCt method. Data is shown as mean ± one standard deviation of three biological replicates. C) Zoom-in from panel B. Deep sequencing was used to quantify the proportion of signal that is derived from edited RNA. D) Top: schematics of deep sequencing approach used to quantify RNA editing. Sequencing reads were aligned to the reference sequence, and modifications at the target site were quantified. Bottom: top five most frequent RNA editing outcomes in PARK7 transcript (guide 2). Dotted lines indicate the positions of RNA breaks by the SthCsm complex. Red dashes depict deletions (Δ) identified in the sequencing data. The proportion of reads with deletions is shown as mean ± one standard deviation of three biological replicates.