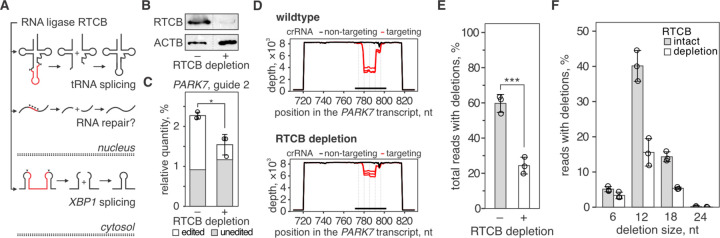
Fig. 2. Depletion of human RNA ligase RTCB restricts the repair of type III CRISPR-mediated RNA breaks.
A) Human RNA ligase RTCB joins RNA ends with a 2′,3′-cyclic phosphate (2’,3’>P) and a 5′-hydroxyl (5’-OH) that are produced by cellular nucleases in tRNA splicing (top) and non-canonical XBP1 mRNA splicing (bottom) during the unfolded protein response. RNA cleavage by SthCsm generates a 2’,3’>P and a 5’-OH at each cut site, and we hypothesized that the ligase activity of RTCB is involved in the RNA repair identified in Fig. 1 (middle). B) Western blot with anti-RTCB or anti-ACTB (loading control) antibodies was performed with lysates of 293T cells with (+) or without (−) RTCB depletion. See the uncropped images in fig. S2. C) PARK7 transcript was targeted with SthCsm (guide 2) in 293T cells with (+) or without (−RTCB depletion. PARK7 transcript was quantified with RT-qPCR and normalized to ACTB non-targeting guide RNA control using the ΔΔCt method. Data are shown as the mean ± standard deviation of three biological replicates. Unequal variances t-test was used to compare mean values. *p-value < 0.05. D) qPCR products in (C) were sequenced, and resulting reads were aligned to the reference sequence of the PARK7 transcript (NM_007262, GenBank). Graphs show sequencing depth (y-axes) at the amplified region of the transcript (x-axes). Every line shows a biological replicate (n = 3). The horizontal black bar indicates a region complementary to the guide RNA of the SthCsm complex. Vertical dotted lines mark predicted positions of RNA breaks. E) Quantification of deletions in target region of the PARK7 transcript. Data is shown as the mean ± standard deviation of three biological replicates. Unequal variances t-test was used to compare mean values. **** p < 0.001. F) The distribution of different deletion outcomes in (D).