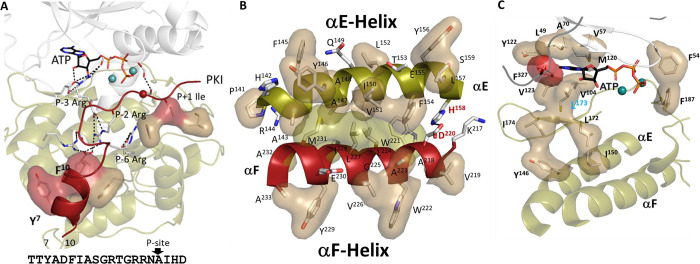
Figure 5. Hydrophobic residues play key roles in PKA.
(A). High-affinity binding of PKI is mediated by the hydrophobic surface of an amphipathic helix and P+1 inhibitor site, both highlighted in red. The sequence of PKI is also shown. (B). Hydrophobic interface between the αE and αF-helices. One side of αF-helix (in red) is shown in tan, and another side in sand, which is the same color coding as Figure 1A. (C). Hydrophobic pocket surrounding ATP. L172, L173, and I174 from β7 anchor this ATP pocket to αE-helix. F327 from C-tail is highlighted in red.