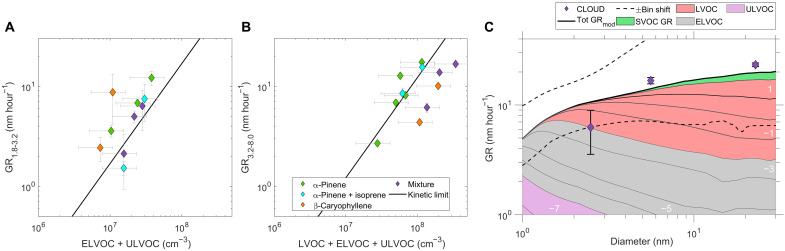
Fig. 5. Growth rates versus vapor concentrations and particle diameter.
Particle growth rates during ozonolysis experiments for (A) particle diameters between 1.8 and 3.2 nm as a function of ELVOC + ULVOC concentrations measured with NO3-CIMS and PTR3 and (B) particle diameters between 3.2 and 8 nm as a function of LVOC + ELVOC + ULVOC concentrations measured with NO3-CIMS and PTR3. The black line shows the geometric limit of kinetic condensational growth for organics (300 Da and density of 1400 kg m−3) (41). (C) Modeled and measured growth rates versus particle diameter for the three-component mixture experiment during ozonolysis at 5°C and 40% RH. The growth rates measured with the DMA-train (differential mobility analyzer train) are shown as diamonds. The error bars show the measurement uncertainty (see the “Particle formation and growth rates” section in Materials and Methods). The color code represents the different VBS bins at 278 K, and their contribution is illustrated by the shaded areas. The uncertainty range on the modeled growth rate calculation is shown as dashed lines, corresponding to a ±1 bin shift of the VBS, i.e., a factor of 10 and 0.1 change of volatility. The contour labels indicate the volatilities of the vapors contributing to particle growth at each size, where white numbers represent the logarithm of the saturation mass concentration (in μg m−3) at 300 K.