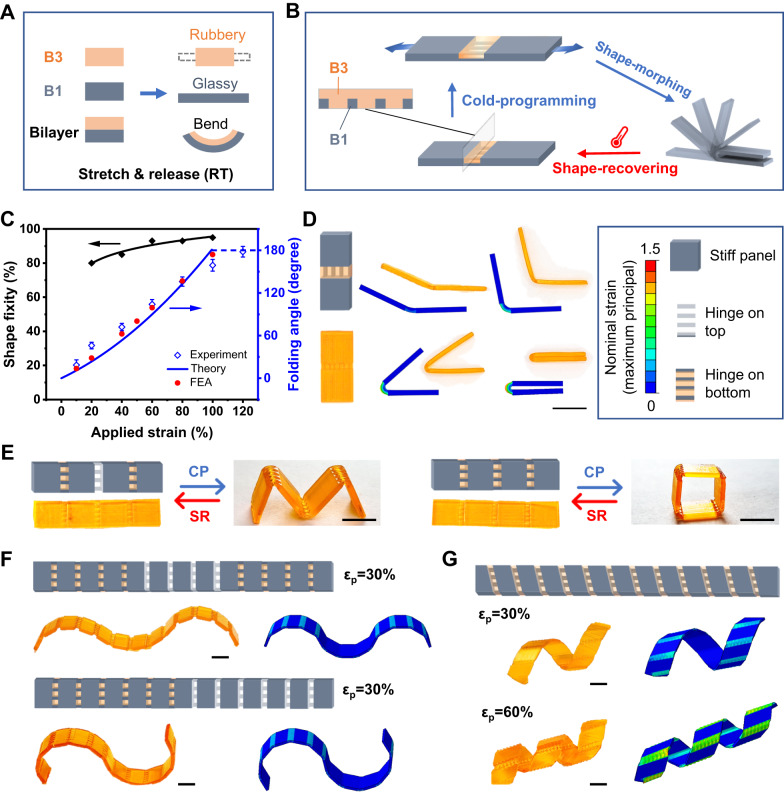
Fig. 2. g-DLP printed cold-programmable hinge.
A Mechanism of the bilayer bending. B Schematic of the heterogenous hinge module design and morphing. C Shape fixity of B1 under different strains and the experiment (error bars are standard deviations based on 5 experimental results), theory prediction, and FEA results of bending angles as the function of the applied strain of the hinge module. D Designed and printed hinge, and the experiment and FEA results of the cold-draw induced bending. E Cold-draw programming (CP) and shape-recovering (SR) of g-DLP printed structures. F Cold-draw programming with different hinge distributions. G Cold-draw programming of helices with 30%(upper) and 60%(lower) strain, respectively. The white color hinge indicates rubbery matrix on the top side, while the orange color hinge indicates rubbery matrix on the bottom side. (F) and (G) share the same color map as (D). All scale bar is 1 cm.