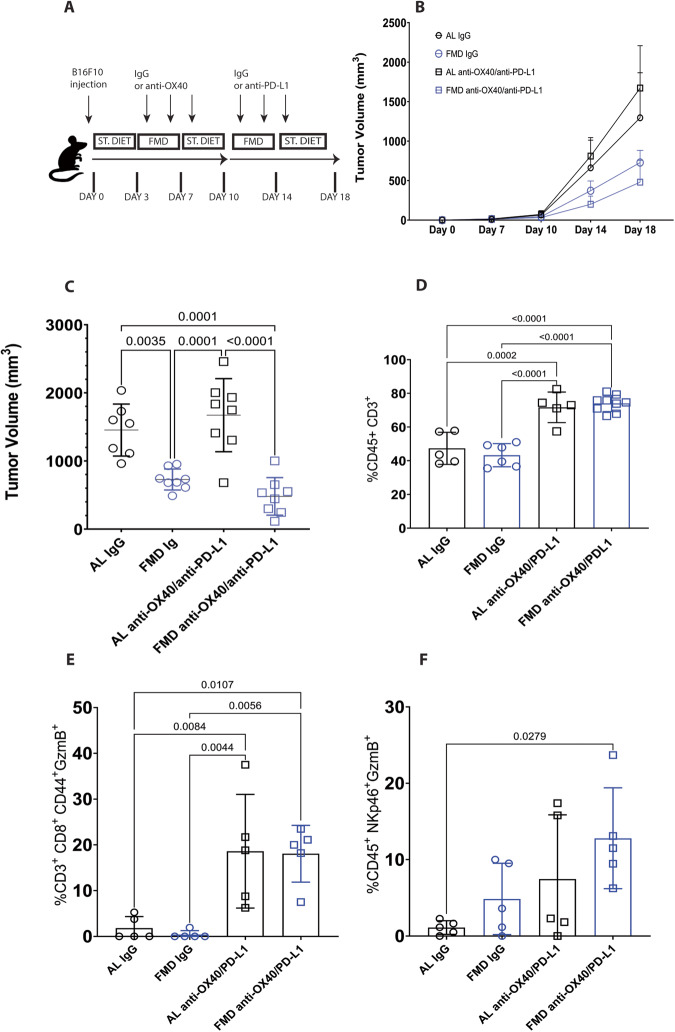
Fig. 2. FMD delays B16 tumor growth and activates NK cells.
A Schedule of tumor implantation and treatment for B16F10 syngeneic tumor models. B, C B16 Tumor growth in immunocompetent C57/j syngeneic mice treated with isotype control and anti-OX40/anti–PD-L1 and fed with standard diet or FMD (AL NT n = 7; FMD NT n = 8; AL anti-OX40/anti-PD-L1 n = 8; FMD anti-OX40/anti-PD-L1 n = 8). D CD45+CD3+ T cell (AL NT n = 5; FMD NT n = 6; AL anti-OX40/anti-PD-L1 n = 5; FMD anti-OX40/anti-PD-L1 n = 9), E CD3+CD8+GzmB+ cytotoxic effector memory T cells (AL NT n = 5; FMD NT n = 5; AL anti-OX40/anti-PD-L1 n = 5; FMD anti-OX40/anti-PD-L1 n = 5, F CD45+NKp46+GzmB+ NK cells (AL NT n = 5; FMD NT n = 5; AL anti-OX40/anti-PD-L1 n = 5; FMD anti-OX40/anti-PD-L1 n = 5). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). P values were determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post analysis. Differences were considered significant when P ≤ 0.05. All data are represented as mean ± SEM. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.