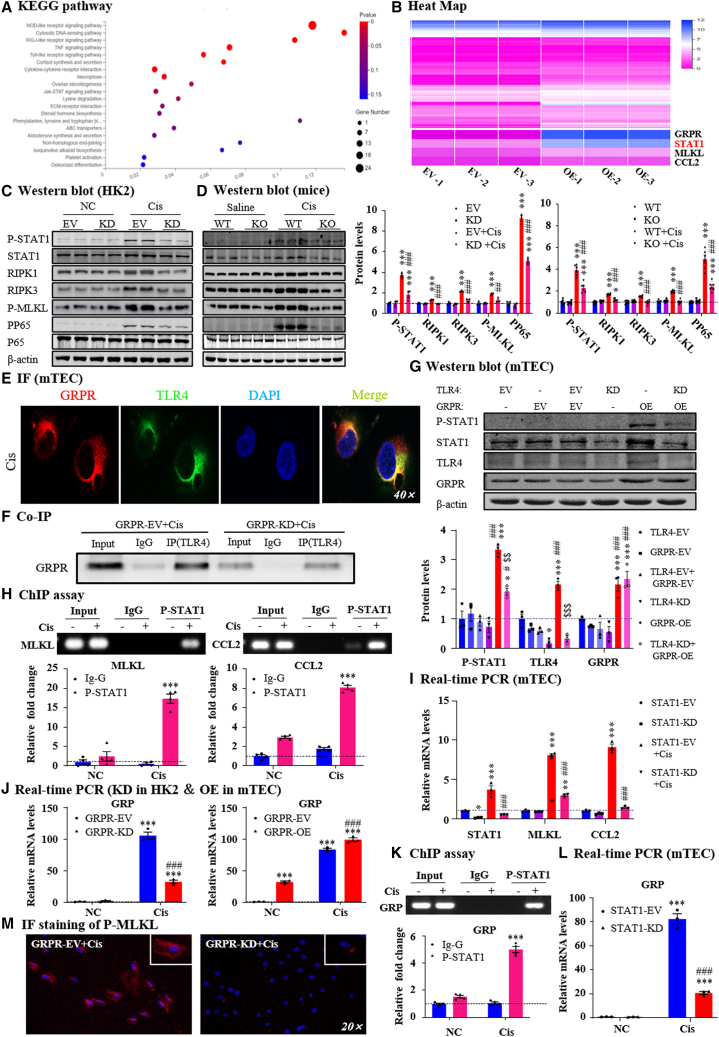
Figure 4.
GRPR promoted renal injury and inflammation in STAT1-dependent mechanisms
(A) KEGG pathway analysis of RNA-seq in GRPR overexpression and control mTECs. (B) Heatmap. (C) Correlated signaling pathways in GRPR knockdown and control HK2 cells. (D) Correlated signaling pathways in GRPR WT and KO mice. (E) IF staining of GRPR and TLR4 in TECs. (F) Co-IP of GRPR and TLR4 in cisplatin-treated TECs. (G) Protein levels of P-STAT1/STAT1/TLR4/GRPR and quantification. (H) The binding of P-STAT1 on MLKL or CCL2 promoter regions were detected by ChIP assay. (I) Relative mRNA levels of STAT1, MLKL and CCL2 in STAT1 knockdown mTECs. (J) The mRNA level of GRP in GRPR knockdown or overexpressed mTECs. (K) The binding of P-STAT1 to GRP promoter by ChIP assay. (L) The mRNA level of GRP in STAT1 knockdown mTECs. (M) IF staining of P-MLKL. Independent experiments were performed throughout the in vitro studies in triplicate. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 vs. EV + NC/WT + saline/TLR4-KD/P-STAT1+IgG. #p < 0.05, ###p < 0.001 vs. EV + Cis/WT + Cis/TLR4-KD/EV + Cis. $$p < 0.01, $$$p < 0.001 vs. GRPR-OE. Cis, cisplatin; EV, empty vector; KD, knockdown; NC, normal control; OE, overexpression; WT, wild type.