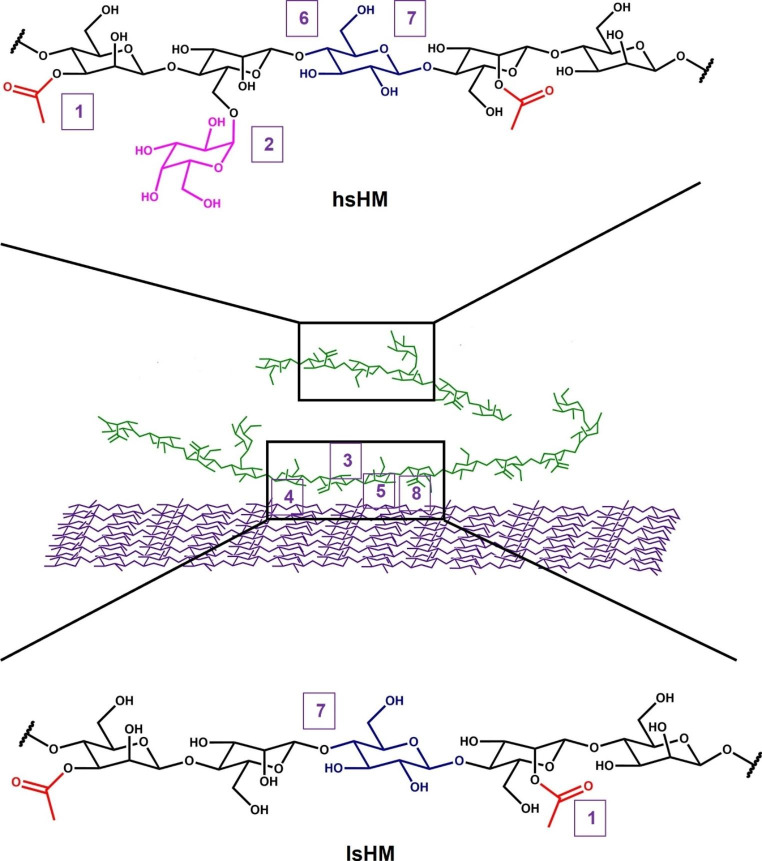
Fig. 3.
A general scheme of how hydrolytic mannanolytic enzymes mechanistically degrade hetero-mannans within lignocellulose in a synergistic fashion with the aid of non-GH proteins, such as CEs, CBMs, expansins, LPMOs and swollenins. The cellulose bound lsHM such as GM regions is degraded by the aid of (1) AcME that removes acetyl groups, (3) CBM may assist in directing key enzymes towards cellulose-mannan junctions, disruption of cellulose-mannan junctions is facilitated by (4) EXP, (5) LPMO and (8) SWO, and oxidative cleavage of mannan by (5) LPMO, and (7) MAN active on GM and linear mannan releases MOS and gluco-MOS. The water soluble hsHM region is degraded by the aid of (2) Aga that removes galactosyl substituents, (6) MBH removes successive mannobiose residues from the non-reducing ends of the mannan, and (7) MAN active on GalM and GM releases MOS, galacto-MOS and gluco-MOS from the mannan. Finally, AcME, Aga, BGL and Mnd act on solubilised O-acetylated MOS, galacto-MOS, gluco-MOS and MOS, respectively (not shown)