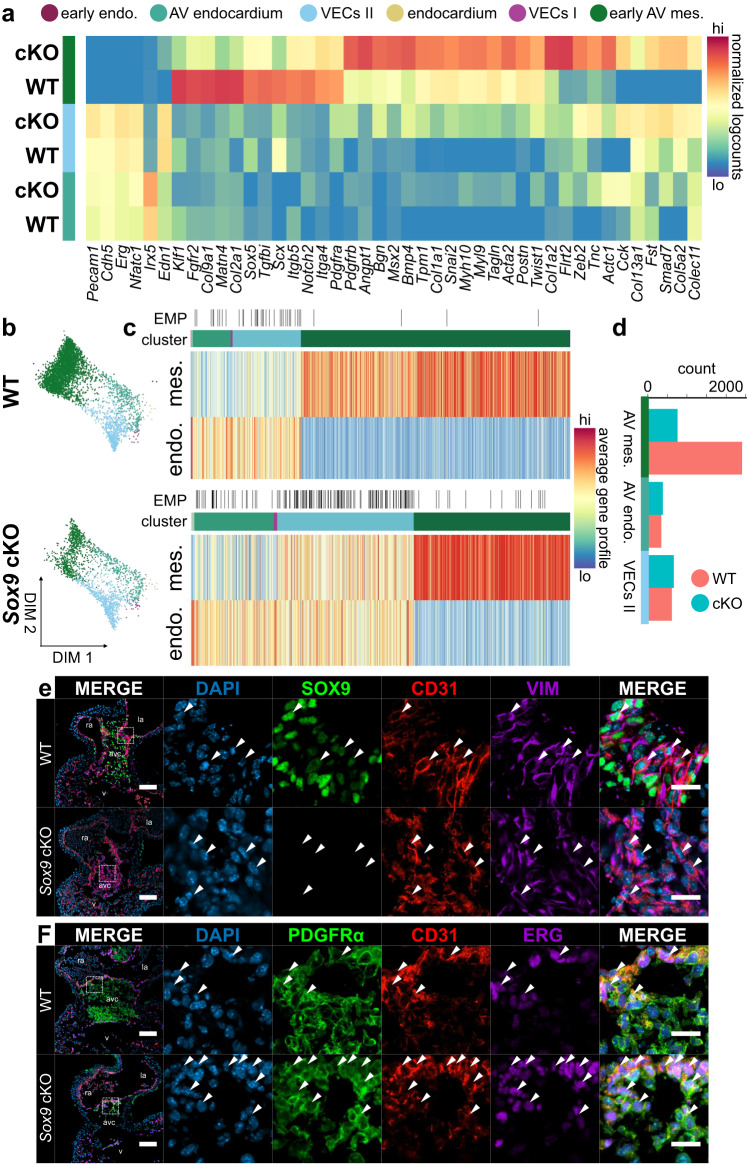
Fig. 4. Perturbations of endothelial and mesenchymal cell states in Sox9 conditional knockout AV canals.
a In the absence of Sox9, differential gene expression analysis reveals profound differences in identity between emergent mesenchymal populations as well as increased expression of mesenchymal factors in VECs. b Force-directed layouts of 3368 WT and 1810 Sox9 cKO endocardial and endocardial-derived cells from E10.5 displaying annotated cluster contribution. c Heatmaps displaying average endothelial and mesenchymal gene profiles for E10.5 WT and Sox9 cKO endocardial and endocardial-derived cells, showing a profound increase in cells exhibiting EMP in the absence of Sox9. d Cell distribution in the three main clusters captured at E10.5 in the WT and Sox9 cKO endocardial-derived lineages, showing reduced numbers of mesenchymal cells in the cKO. Comparing (e) SOX9, CD31, and vimentin or (f) PDGFRα, CD31, and ERG immunostaining in E10.5 Sox9 cKO and WT AV canals reveals developmental arrest of endocardial cells with mesenchymal features, like VIM or PDGFRα (white arrowheads). Few fully transdifferentiated mesenchymal cells lacking CD31 expression are observed in the Sox9 cKO. Results are representative of three to six independent experiments. Scale bars: 100 µm, 25 µm in ROIs. AV atrioventricular, endo. endothelium, mes mesenchyme. See also Supplementary Fig. 4 and Supplementary Data 2 and 4. Source Data are provided as a Source Data file.