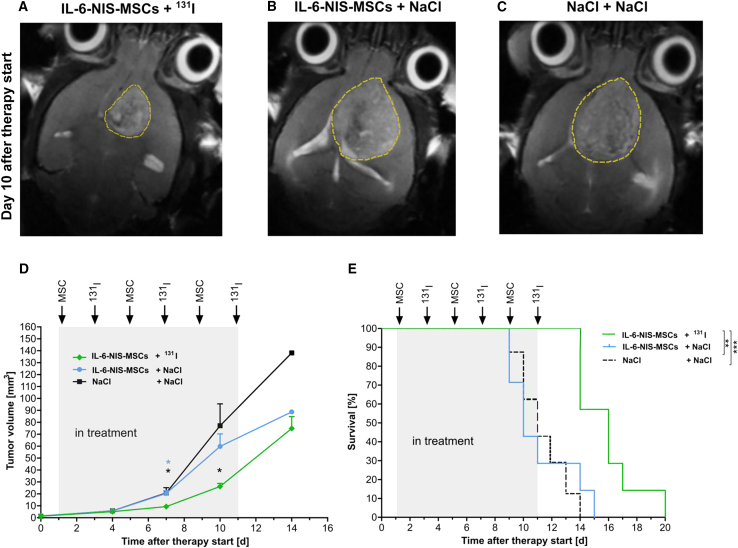
Figure 5.
IL-6-targeted MSC-mediated NIS gene 131I therapy of GBM-bearing mice led to reduced tumor growth and improved survival
Three cycles of a single i.v. IL-6-NIS-MSC injection was applied followed by an i.p. administration of 131I 48 h later (MSCs on days 1/5/9 and 131I on days 3/7/11, respectively). Representative MR images 10 days after therapy start are shown after treatment with (A) IL-6-NIS-MSCs + 131I, (B) IL-6-NIS-MSCs + NaCl, and (C) NaCl + NaCl. (D) Tumor growth was monitored using MRI showing a significantly reduced tumor mass of IL-6-NIS-MSCs + 131I as compared with controls after completion of two therapy cycles (day 7 after treatment start, n = 7 each, ∗p < 0.05). At day 10 after therapy start, tumor growth of mice from the therapy group (n = 7/7) was delayed as compared with the NaCl-only group (n = 6/7, ∗p < 0.05) and the IL-6-NIS-MSC + NaCl-treated mice (n = 5/7, ns). Fourteen days after therapy start, all mice from the therapy schedule were included in the tumor measurement (n = 7/7), but n = 3 had to be euthanized the same day, while in the NaCl-only group only n = 1 of 7 and the IL-6-NIS-MSC + NaCl n = 2 of 7 of the mice were still alive and included in the measurement. (E) The survival of IL-6-NIS-MSCs + 131I-treated mice was significantly extended as compared with the controls treated with NaCl + NaCl (∗∗∗p < 0.001) and IL-6-NIS-MSCs + NaCl (∗∗p < 0.01). Tumors are encircled in yellow dotted lines and results are expressed as mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA using Tukey’s post hoc test was performed for tumor growth analysis and log rank test for comparison of survival curves.