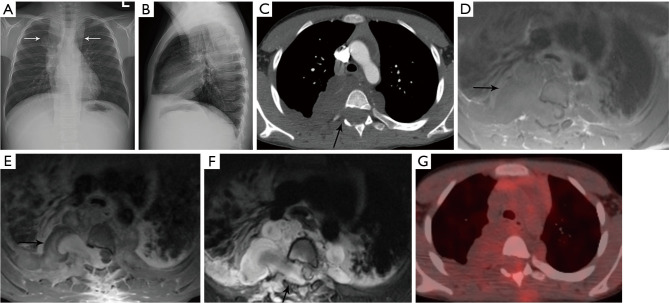
Figure 10.
Ganglioneuroma. (A,B) PA and lateral chest radiographs show elongated bilateral posterior mediastinal lesion (arrows) extending from the neck down to below the diaphragm. (C) Axial contrast enhanced CT shows bilateral paraspinal masses with low attenuation and enlargement of the right neural foramen of T4 (arrow) with extension into the spinal canal. (D) Axial T1-weighted MRI shows the mass (arrow) is heterogeneous with iso- to hyperintense signal. Extension into the spinal canal displaces and the spinal cord to the left with abnormal signal intensity within the cord due to cord compression and edema. (E) Axial T1-weighted post-contrast MRI shows the mass (arrow) enhances heterogeneously. (F) Axial T2-weighted MRI shows the mass (arrow) is heterogeneously hyperintense. (G) Fused PET/CT shows the ganglioneuroma is not FDG avid. Biopsy confirmed ganglioneuroma. PA, posterior anterior; CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; PET, positron emission tomography; FDG, fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose.