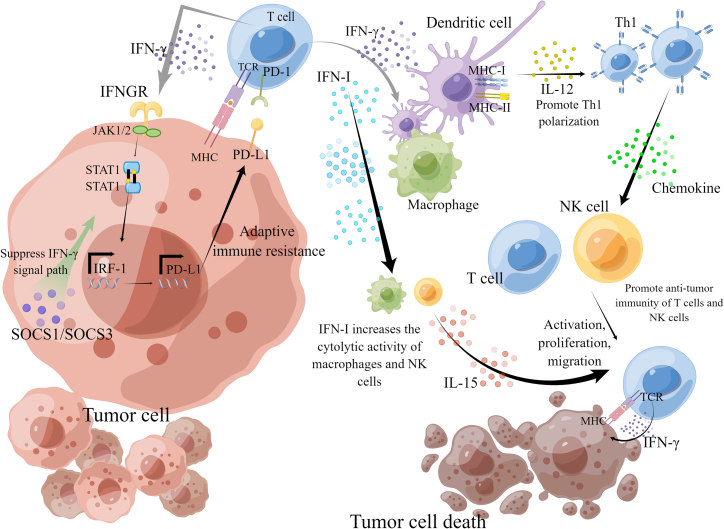
Figure 1.
The main action pathway of IFN in inhibiting tumor cells
IFN-I can activate DCs, increase the cytolytic activity of macrophages and NK cells, induce the production of IL-15, activate T cells, and increase the survival of T cells. The IFN-γ signal cascade pathway is the main anti-tumor pathway of IFN-II. IFN-γ binds to IFN-γ receptors (IFNGRs) on tumor cells and stimulates Janus kinase (JAK) signal transduction and transcription (STAT) activator signaling pathway, which stimulates phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of STAT1, thus activating the IFN-stimulated gene transcription program and regulating the immune response. IFN-γ enhances the production of MHC-I and MHC-II in cancer cells and IL-12 in APC, promotes Th1 polarization, and promotes tumor transport of immune cells through the secretion of Th1 chemokines, thus achieving the anti-tumor purpose.