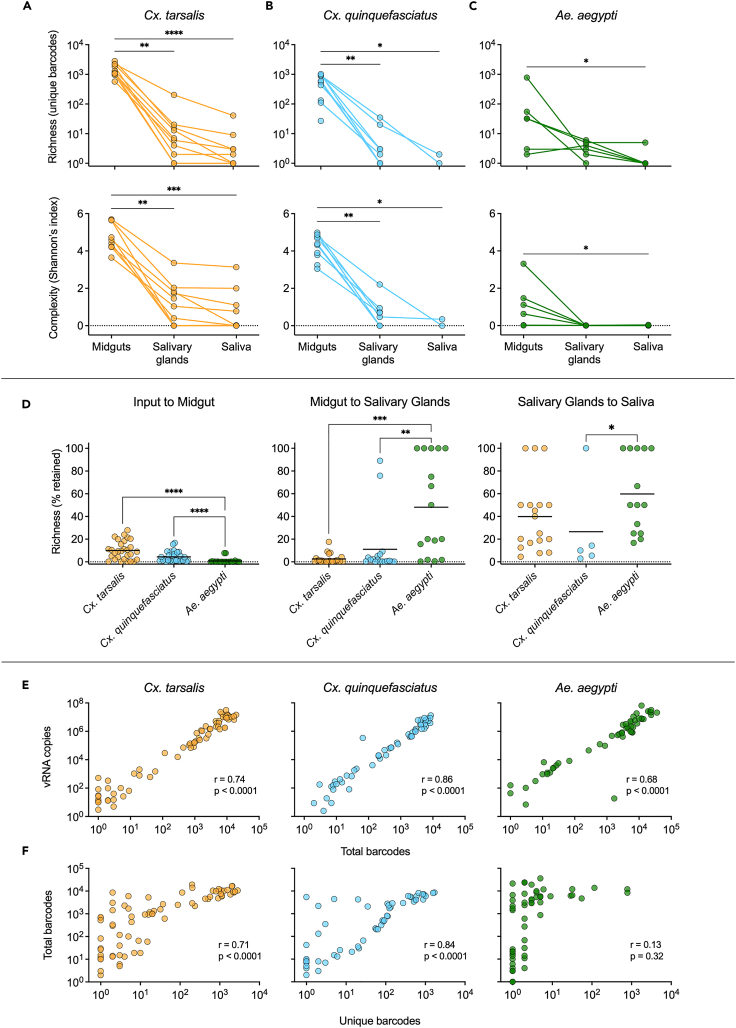
Figure 3.
Quantifying the impact of intrahost bottlenecks on population richness and complexity
(A–C) 8-day post-infection bcWNV population richness and complexity in midgut, salivary gland, and saliva samples from Cx. tarsalis (A), Cx. quinquefasciatus (B), and Ae. aegypti (C) mosquitoes. Lines connecting points indicate that samples were collected from the same mosquito. Diversity indices were generated by applying the Shannon function from the QSutils package in R to barcode abundance vectors. Dashed line represents 0.
(D) Percent of preceding unique barcode population retained after each bottleneck in each species (all timepoints included). Solid lines denote mean. (A-D) Statistical significance determined using Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test, ∗ = p < 0.05, ∗∗ = p < 0.005, ∗∗∗ = p < 0.0005, ∗∗∗∗ = p < 0.0001. Only significant comparisons shown.
(E) Pearson’s correlation between vRNA and total barcodes, and (F) unique and total barcodes in all samples from each species. Pearson’s r values and significance values are displayed on plots.