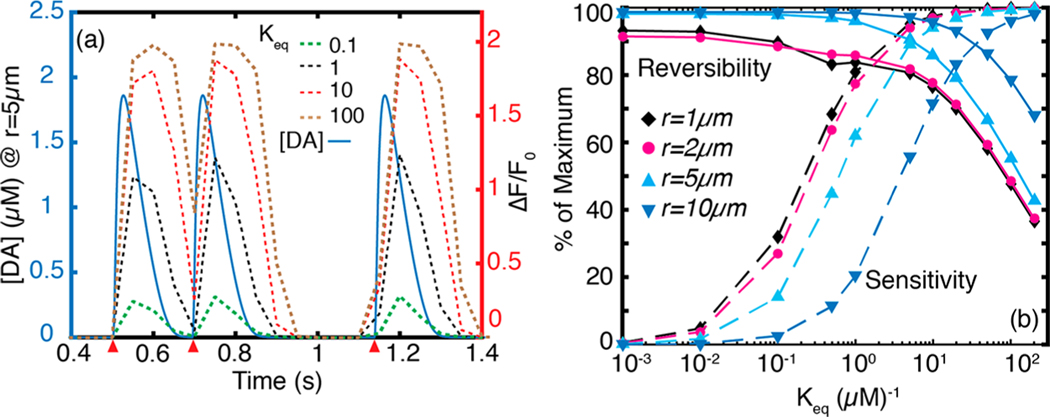
Figure 5.
Effect of nanosensor parameter on performance. (a) Dynamics of three quantal release events (red wedges) imaged using nanosensors for which varies over 3 orders of magnitude. The first two quantal releases are located 0.2 s apart. Plots of for a 20 Hz frame rate (eq 10) corresponding to each value are plotted in dashes. At , the nanosensor affinity for dopamine is too strong, which adversely affects reversibility. The second release event cannot be resolved. Peak values increase with increasing . At low values, the nanosensor shows high reversibility but poor sensitivity. (b) Parameter space for reversibility and sensitivity at , and 10 μm from release site corresponding to a 20 Hz imaging frame rate. High dopamine concentrations proximal to the release site yield high percent nanosensor sensitivity. However, maintaining good nanosensor reversibility suffers proximal to the release site.