Figure 1. Dimethyl labeling of bovine serum albumin (BSA) combined with multiplexed data‐independent acquisition (mDIA).
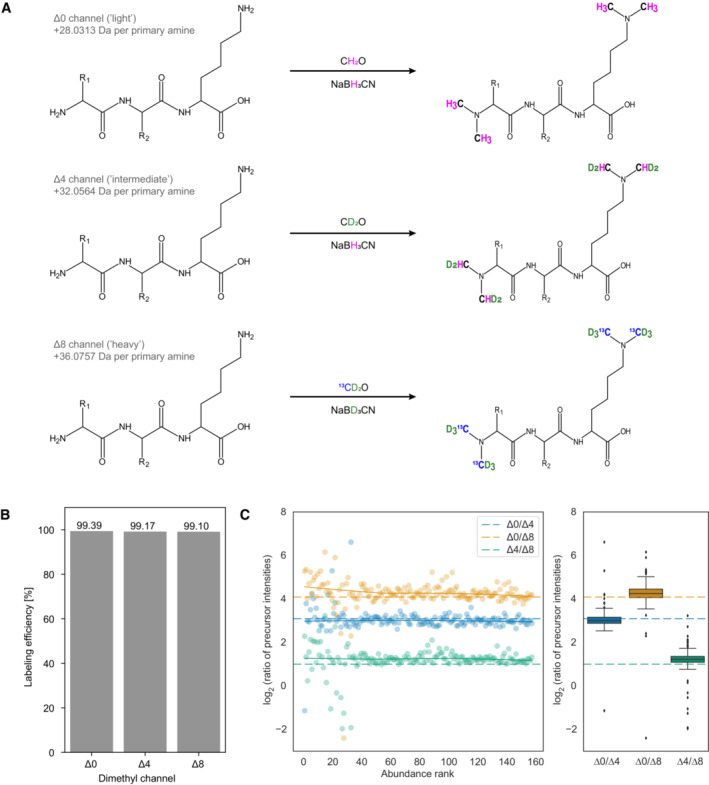
- Stable isotope dimethyl labeling scheme for a three‐plex mDIA setup. Six hydrogens can be replaced by deuterium and the two carbons by 13C per dimethyl, of which there are one in tryptic peptides ending in arginine (N‐terminus) and two in those ending in lysine (N‐terminus and N‐ε‐Lys). Depending on the combination of stable isotope labeling reagents, mass tags of 28.0313 Da, 32.0564 Da, or 36.0757 Da are added to each primary amine group of a peptide. A tryptic peptide harboring a C‐terminal lysine residue is depicted.
- Dimethyl labeling efficiency of peptides derived from intensity ratios of labeled peptides relative to all detected peptides in DDA mode (n = 1).
- Quantification accuracy of dimethyl labeled peptides in DIA mode. Differentially labeled tryptic BSA peptides were mixed in a 17:2:1 ratio of Δ0/Δ4/Δ8 and the data was acquired in DIA mode. Scatterplots (left) illustrate the log2 intensity ratios as a function of the peptide abundance rank, which is summarized as a boxplot (right). The box depicts the interquartile range with the central band representing the median value of the dataset. The whiskers represent the furthest datapoint that is within 1.5 times the interquartile range (IQR). In both panels, the expected ratios are marked by colored dashed lines. 50 fmol BSA was injected per replicate (technical replicates, n = 3).
