FIGURE 1.
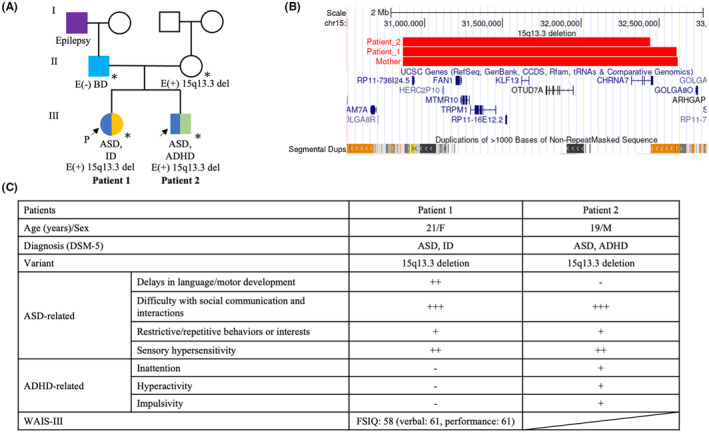
Clinical data of the patients and their parents. (A) The pedigree of this family. The 15q13.3 deletion was inherited from a healthy mother to two affected siblings (Patient 1 and patient 2). (B) Visualization of the 15q13.3 deletions in this family. The regions and sizes of the 15q13.3 deletions are, chr15:30861184–32 620 098, 1 758 914 bp (mother), chr15:30861184–32 610 833, 1 749 649 bp (Patient 1) and chr15:30861184–32 443 327, 1 582 143 bp (Patient 2). The genes affected by the 15q13.3 deletion are RP11‐736I24.5, HERC2P10, FAN1, MTMR10, TRPM1, RP11‐16E12.2, KLF13, OTUD7A and CHRNA7. (C) This table shows the summary of the clinical findings of the siblings. Although their CNV was the same, the phenotype of these patients was different at some points; only patient 1 had ID, and only patient 2 had ADHD. The severity of each psychiatric symptom was graded with 3 levels by a board‐certified research psychiatrist, based on the ADI‐R results: + (mildly present), ++ (moderately present), and +++ (strongly present). ADHD, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; ADHD; DSM‐5, Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5th Edition; ASD, autism spectrum disorder; BD, bipolar disorder; FSIQ, Full Scale IQ; ID, intellectual disability; WAIS‐III, Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale‐III.
