Figure 2. Neutrophil heterogeneity in respiratory tract.
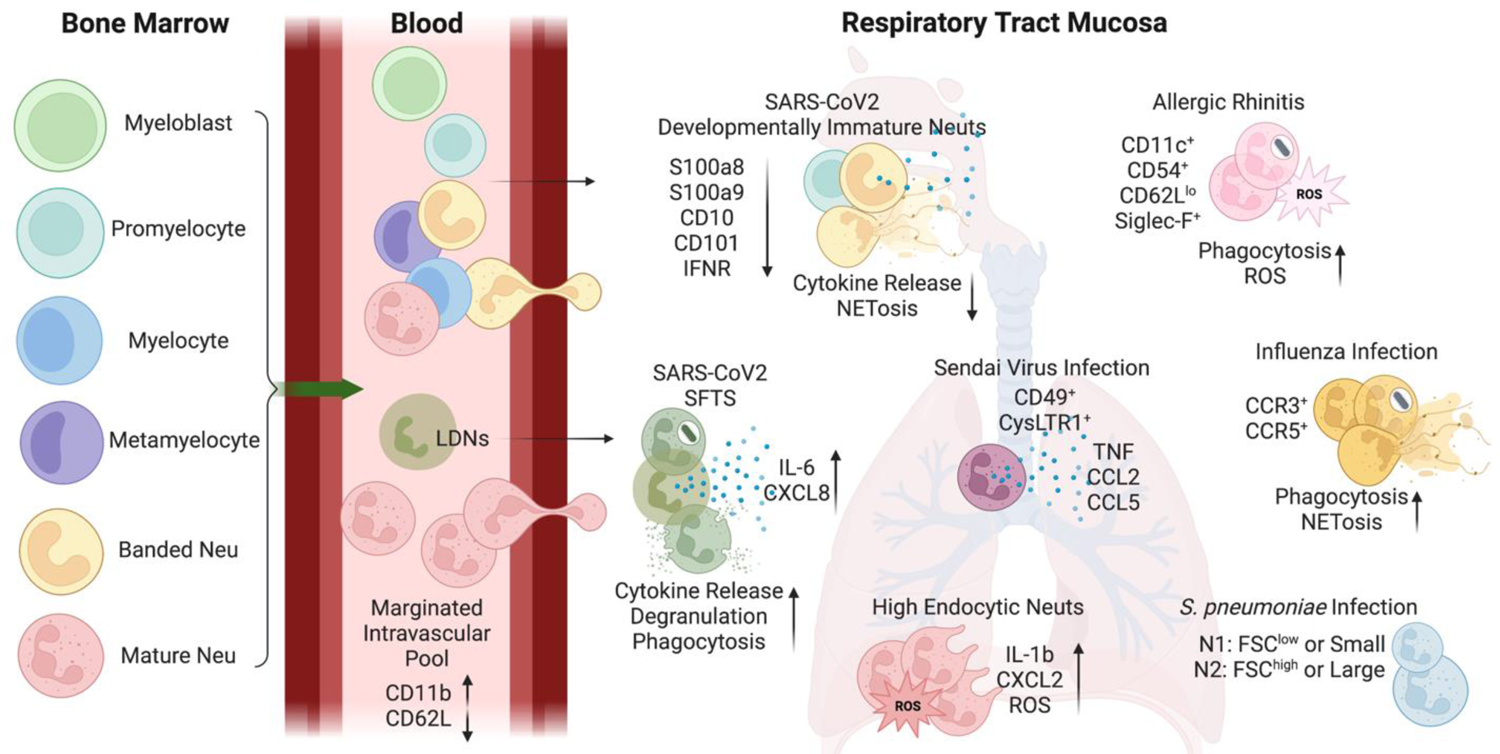
Developmentally divergent neutrophils (Neu) have been detected in the circulation and respiratory tract mucosa during inflammatory conditions. Lungs contain a marginated intravascular pool of neutrophils with tissue-specific marker expression. Additionally, immature neutrophils and low-density neutrophils (LDNs) have been identified in the respiratory mucosa during disease states. Furthermore, select neutrophil subtypes have been identified in distinct infections. These subsets may exert various effector functions with different capabilities.
C-C motif chemokine ligand (CCL); C-C motif chemokine receptor (CCR); cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 (CysLTR1); C-X-C chemokine receptors (CXCR); forward scatter (FSC); interferon receptor (IFNR); interleukin (IL); neutrophil extracellular trap formation (NETosis); reactive oxygen species (ROS); S100 calcium binding protein A (S100A); severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS); tumor necrosis factor (TNF)
