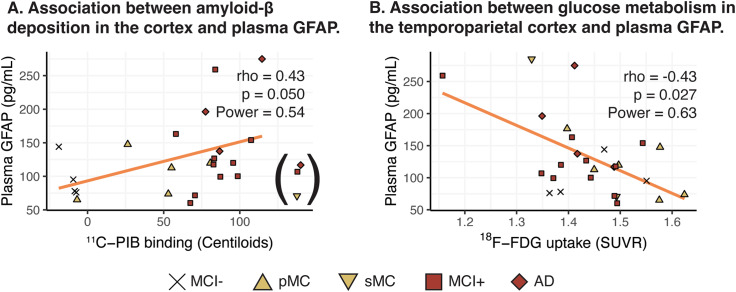
Fig. 4.
Cross-sectional correlation analyses evaluating the relationship between 11C-PIB, 18F-FDG PET tracers’ binding/uptake and plasma GFAP. The analyses were performed for composite cortical ROIs (A, B) in the whole sample, not considering the non-carrier group. For the correlation analyses between 11C-PIB binding and plasma GFAP levels, the individuals with extremely high 11C-PIB binding (marked in parentheses in the figures) were excluded given the known non-linear association between the biomarkers in high amyloid-β levels [48]. For the analyses pertaining to 11C-PIB binding, APParc mutation carriers were excluded due to the known mutation-specific relative sparsity of fibrillar amyloid-β that causes exceptionally low 11C-PIB binding levels. The Spearman’s correlation coefficient (rho), the p and power values are shown. NC: non-carriers; pMC: presymptomatic mutation carriers; sMC: symptomatic mutation carriers; MCI-: MCI with a negative amyloid-β PET scan; MCI+: MCI with a positive amyloid-β PET scan; AD: Alzheimer’s disease dementia