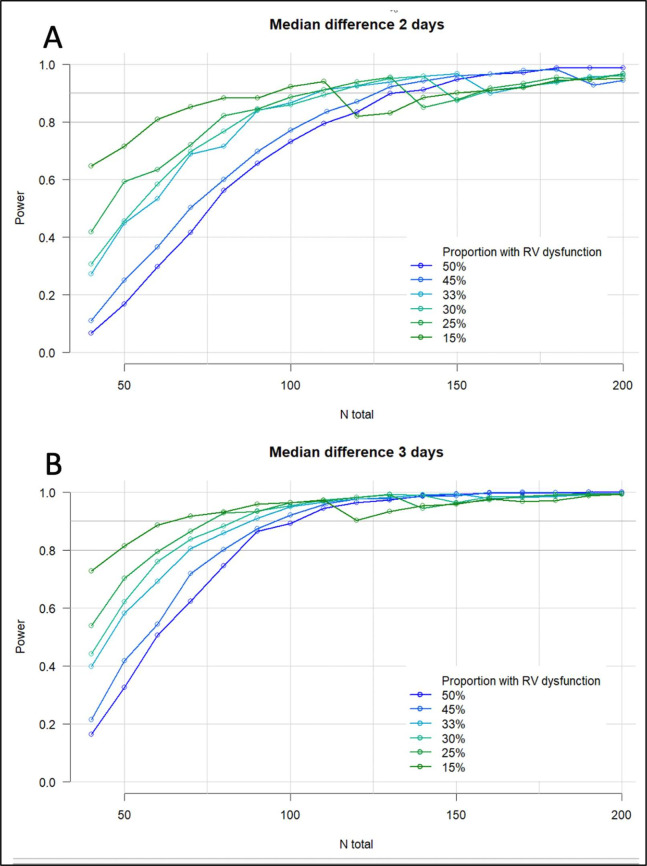
Figure 2.
Simulated power analysis for impact of RVD on days alive and at home at 30 days. Assuming for 1% of the patients DAH30=0, for the remainder DAH30 follows a negative binomial distribution with parameters chosen such that the median DAH30 is 24/25 in one group and 27 in the other group and the shape of the distribution is similar to that seen in the validation cohorts. The simulated DAH30 was then compared between groups using negative binomial regression (repeated) in 1000 samples. The figures show the resulting estimated power for incidences of postoperative RVD from 15% to 50%#, and for a clinical effect size of 2 (A) or 3 (B) days difference in DAH30*. #In our previous work the incidence of postoperative RVD was 50% in thoracic surgical patients but may be significantly less in, for example, an orthopaedic population. *In Chou et al’s study preoperative RV dysfunction prolonged hospital length of stay by over 50%, but this cohort was a very high-risk vascular surgical population.7 DAH30, days alive and at home at 30 days postoperatively; RVD, right ventricular dysfunction.