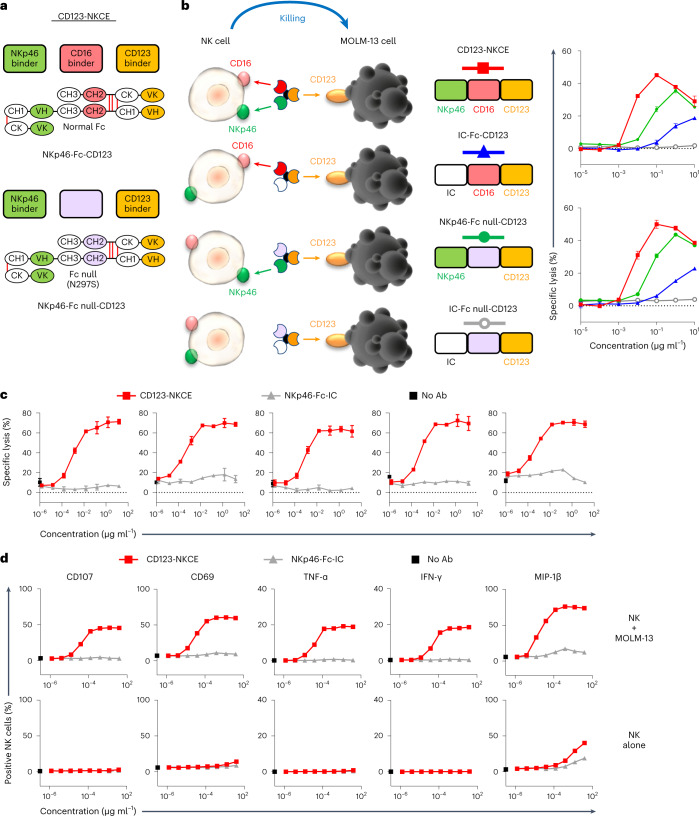
Fig. 2. CD123-NKCE displays strong cytotoxic activity against AML cells, strong activation of NK cells and no off-target effects.
a, Diagrams showing the molecular organization of the NKCE molecules. The top shows the CD123-NKCE trifunctional molecule built with an unmodified human IgG1-Fc (red), targeting CD123 (orange) and coengaging NKp46 (green) and CD16a on NK cells. The bottom shows the bifunctional NKCE containing a human IgG1-Fc silenced for binding to all FcγRs (Fc null; purple). b, Comparison of the cytotoxicities of NKCEs targeting CD123 and engaging CD16a only (IC-Fc-CD123), NKp46 only (NKp46-Fc null-CD123) or coengaging NKp46 and CD16a (NKp46-Fc-CD123; CD123-NKCE). MOLM-13 cells were used as the targets and purified resting NK cells as effectors. Results for two healthy donors are shown (n = 3). Data are presented as mean values ± s.d. c, Cytotoxicity of CD123-NKCE against the AML cell line MOLM-13. Results for five healthy donors are shown. Data are presented as mean values ± s.d. d, Evaluation, by flow cytometry, of CD107, CD69, TNF-α, IFN-γ and MIP-1β expression by NK cells treated with CD123-NKCE. NK cells alone are compared with NK cells cocultured with MOLM-13 cells. Results for one representative donor are shown (n = 3).