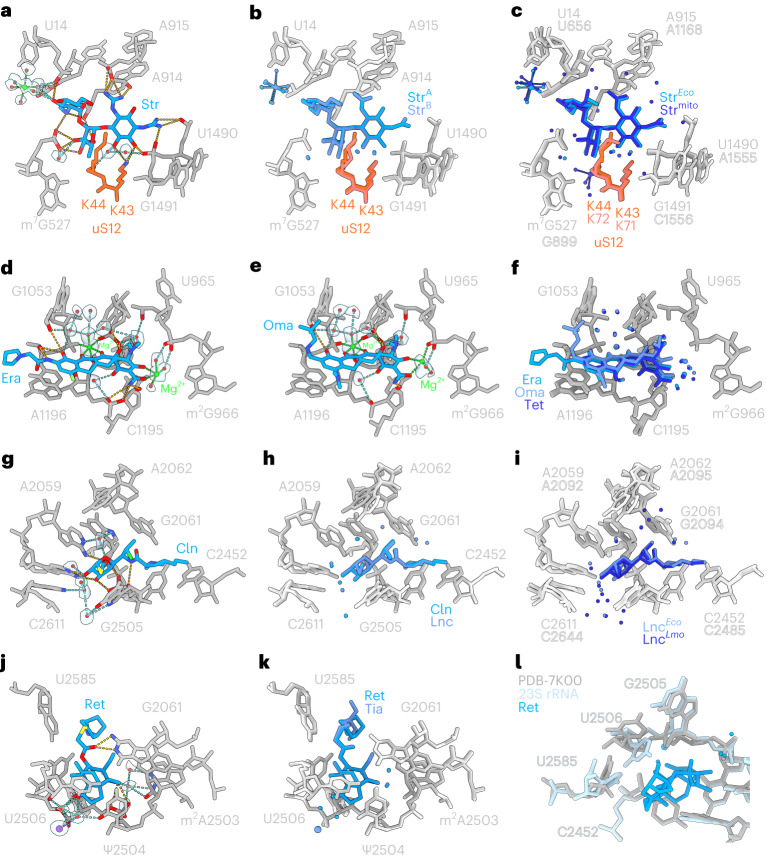
Fig. 4. Structural conservation of antibiotic binding to ribosomes.
a, Interaction of streptomycin (StrA) on the SSU at 2.0 Å. b, Superimposition of streptomycin (StrA) from a with streptomcyin (StrB) determined at 1.8 Å (from Fig. 2). c, Superimposition of streptomycin determined here on E. coli (StrEco) at 1.8 Å (StrB from Fig. 2) with streptomycin on the human mitochondrial SSU body (Strmito) at 2.23 Å (ref. 11). d,e, Interaction of eravacycline (Era) (d) and omadacycline (e) on the SSU at 2.1 and 2.2 Å, respectively. f, Superimposition of eravacycline (Era) from d, omadacycline from (and tetracycline (Tet) (from Fig. 2). g, Interaction of clindamycin (Cln) on the LSU at 2.0 Å. h, Superimposition of clindamycin (Cln) from g with lincomycin (Lnc) determined at 1.6 Å (from Fig. 3). i, Superimposition of lincomycin determined here on E. coli (LncEco) at 1.8 Å (from Fig. 2) with lincomycin on the L. monocytogenes 70S ribosome (LncLm. at 2.1 Å, ref. 47). j, Interaction of retapamulin (Ret) on the LSU at 1.9 Å. k, Superimposition of retapamulin (Ret) from j with tiamulin (Tia) (from Fig. 3). l, Superimposition of Ret (blue) and 23S rRNA (cyan) from Ret-LSU structure with E. coli 70S ribosome lacking any drug in the A-site of the PTC (gray, PDB ID 7K00)12.