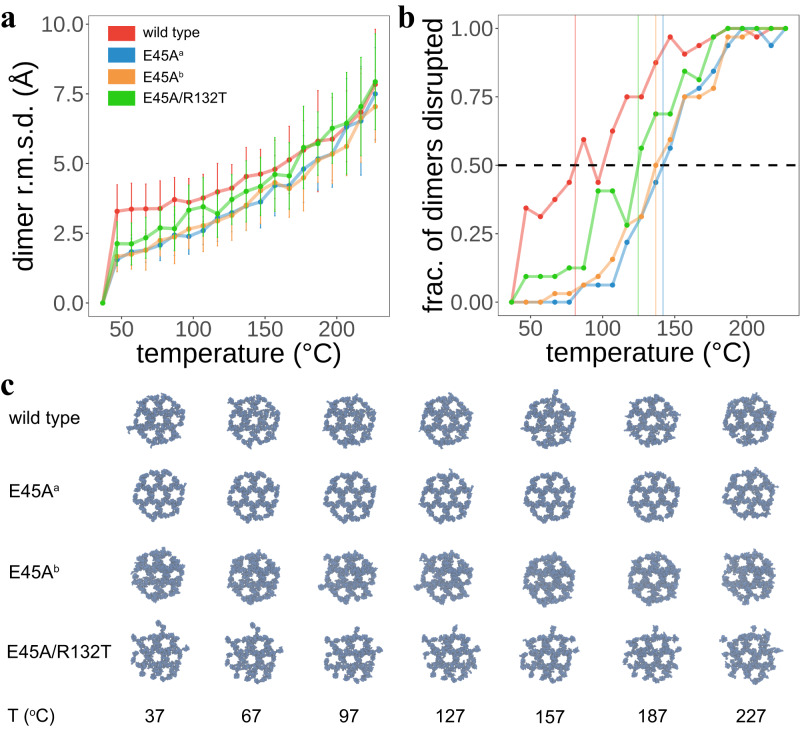
Fig. 4. In silico thermal stability assay of WT and mutant CA lattices.
a Dimer interface RMSD analysis for 2 × 3 × 3 hexameric CA lattices. Four constructs, WT, E45Aa, E45Ab, and E45A/R132T, were subjected to tempering simulations. Temperatures employed for NPT simulations were between 310 K and 500 K with a stride of 10 K. The RMSD is presented as the mean and standard deviation, of all dimers in each lattice (n = 32 dimer interfaces from each 2 × 3 × 3 hexameric lattice simulation), between backbone atoms comprising the interface. The reference structures were taken as the respective dimer interface simulated at 310 K. This reference point is included in the plot for clarity. b Tm profiles for all CA lattice constructs, based on the RMSD data shown in a. Based on the RMSD analysis, we consider a dimer interface to be disrupted if it deviates from its 310 K reference structure with a heavy-atom RMSD > 3.5 Å. Tm is the temperature where half of the dimer interfaces in the lattice are disrupted. This is visible as the point of intersection between the traces and the horizontal dashed line at a y-axis position of 0.5. For WT, this is 81.0 °C; for E45Aa and E45Ab, these are 141.8 and 136.9 °C, respectively; for E45A/R132T, this is 124.6 °C. c Snapshots of 1 × 3 × 3 lattice CTDs taken at select intervals across the temperature range sampled, providing a qualitative view of the lattice stability. E45Aa is robust even at the highest simulation temperatures. Snapshots of NTDs and CTDs for every temperature are shown in Supplementary Fig. 10.