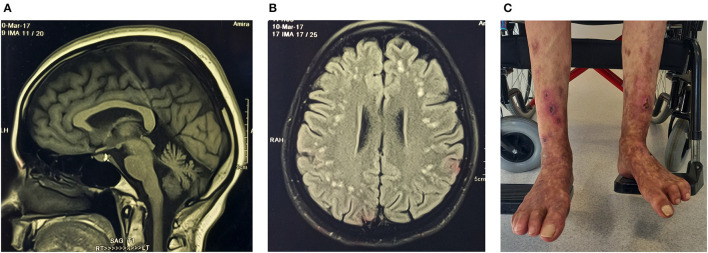
Figure 3.
Proband (ICGNMD_8) with a milder phenotype of RFT1-congenital disorder of glycosylation. Brain imaging at age 35 years. (A) Sagittal T1-weighted MRI-brain scan showing cerebellar atrophy. (B) An axial brain FLAIR MRI image showing widespread discrete high signal intensity lesions in the subcortical white matter. Apart from the RFT1-disorders known to have coagulation factor abnormalities, the patient had no other cardiovascular risk factors to account for these white matter abnormalities of presumed vascular origin. (C) Spontaneous painful lesions with subsequent ulceration, which occurred in the distal extremities (before anticoagulation). Since oral anticoagulants were started for possible clotting abnormalities as a cause, the lesions have disappeared in the forearms and are substantially less in the legs (age 49).