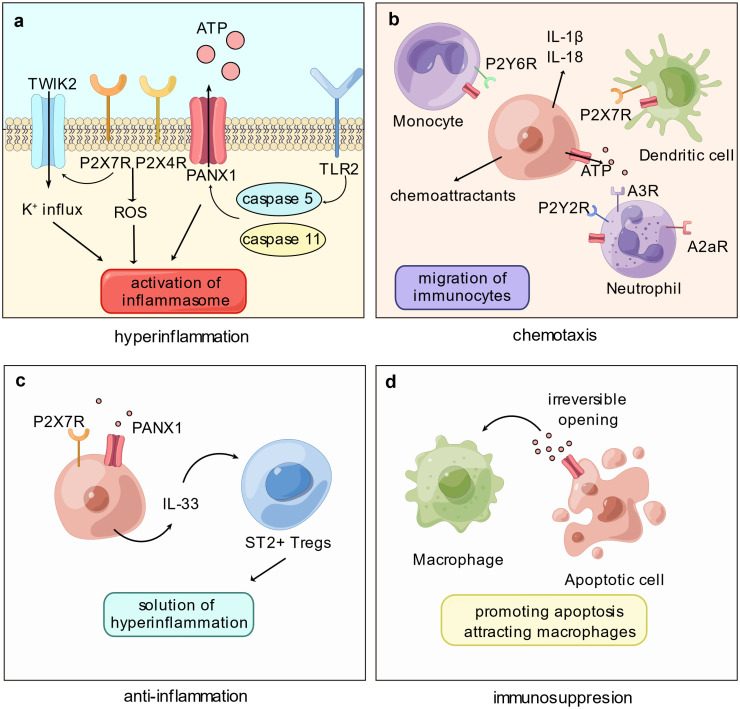
Figure 1.
Panx1 participates in immune disorder by proinflammation and immunosuppression. (A) The proinflammatory role of Panx1 is associated with activation of the inflammasome. Cleavage of Panx1 by caspase proteins, such as caspase-5 or -11, opens Panx1 and leads to downstream signaling pathways that activate inflammasome: Purinergic stimulation on P2X7R and P2X4R promotes the production of cytoplasmic ROS; P2X7R mediates the K+ influx via TWIK2 channel. (B) Opening of Panx1 recruits immune cells mainly via the purinergic signaling pathway. ATP released via Panx1 attracts monocytes, neutrophils, and dendritic cells, meanwhile Panx1 on immune cells mediates migration. Release of proinflammatory molecules or chemoattractants promoted by Panx1 hemichannel activation, such as IL-1β and IL-18, certainly elevates immunocyte migration. (C) Panx1 contributes to immunosuppression by mediating the production of IL-33. As an immunoregulatory molecule, IL-33 binds ST2+ Tregs and assists resolution of hyperinflammation. (D) Activation of Panx1 hemichannel elevates apoptosis level of immune cells, promoting immune paralysis. Further, ATP released by Panx1 acts as “find-me” signals and attracts macrophages.