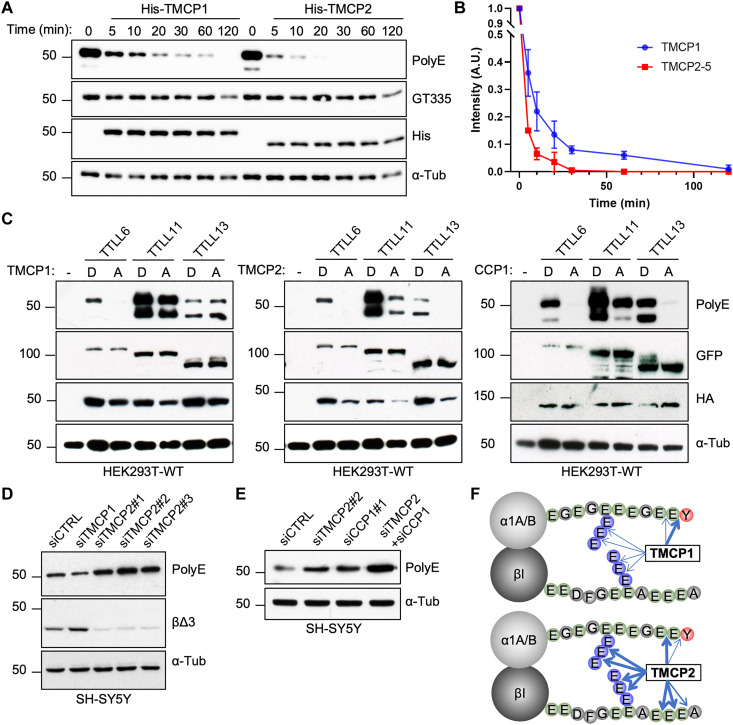
Fig. 6. TMCPs catalyze the removal of posttranslational polyglutamylation.
(A) Immunoblots of an in vitro deglutamylation assay measuring time-dependent activity of recombinant His-TMCP1 and His-TMCP2 toward MTs derived from mouse brain. (B) Graphical representation of His-TMCP1 and His-TMCP2 deglutamylase activities. Immunoblot signals (polyE antibody) were quantified for each time point (mean ± SD; n = 3 independent experiments). (C) Immunoblots of protein extracts from HEK293 cells coexpressing GFP-TTLL6, GFP-TTLL11, or GFP-TTLL13 in the presence of either active or enzymatically dead HA-TMCP1, HA-TMCP2, and HA-CCP1. (D) Immunoblots of protein extracts from SH-SY5Y cell knockdown for TMCP1 or TMCP2. Three different siRNAs were used for TMCP2, one siRNA for TMCP1, and a scramble siRNA as control. (E) Immunoblots of protein extracts from SH-SY5Y cells following knockdown of TMCP2 or CCP1, either alone or in combination. (F) Schematic overview of α- and β-tubulin modifications catalyzed by TMCP1 and TMCP2. The width of the arrows represents the cleavage efficiency.