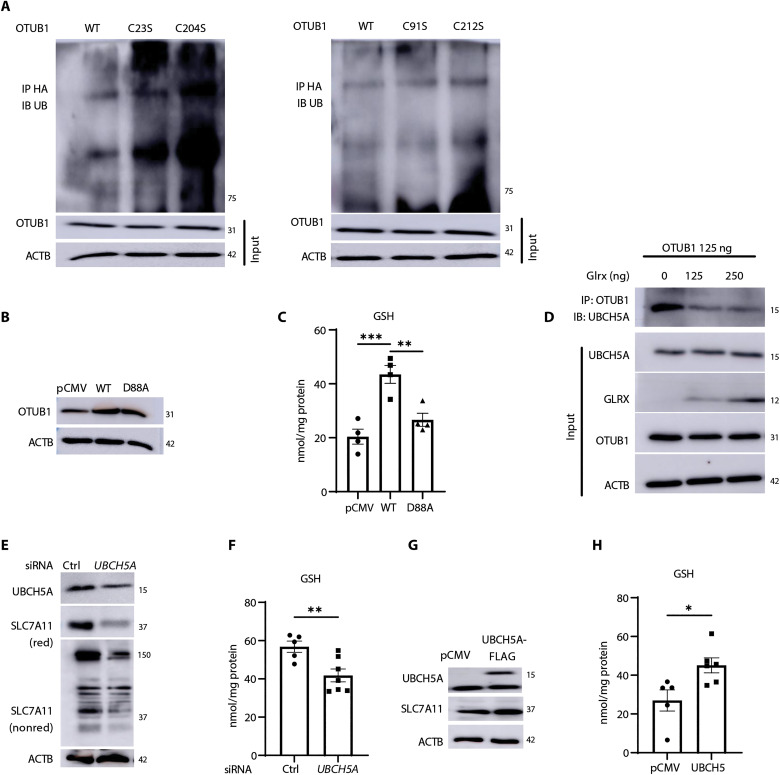
Fig. 7. The E2-conjugating enzyme, UBCH5A, interacts with OTUB1 in a GLRX-sensitive manner to increase SLC7A11 and GSH.
(A) Levels of ubiquitinated SLC7A11 in H522 cells transfected with OTUB1-WT, OTUB1-C23S, or OTUB1-C204S (left) and OTUB1-WT, OTUB1-C91S, or OTUB1-C212S (right) and treated with 40 μg of MG-132 for 4 hours. OTUB1 and ACTB from total cell lysates were used as input controls. (B) Confirmation of expression of OTUB1-WT, OTUB1-D88A, or pCMV vector plasmids via Western blot analysis. ACTB, loading control (C) Assessment of GSH levels in H522 cells overexpressing OTUB1-WT or OTUB1-D88A plasmids or pCMV vector control. (D) Effect of overexpression of GLRX for the interaction between UBCH5A and OTUB1. OTUB1 was immunoprecipitated followed by detection of UBCH5A via Western blotting. Input: GLRX, UBCH5A, and OTUB1 levels in whole-cell lysates used for immunoprecipitation. ACTB, loading control (E) Impact of SiRNA-mediated knockdown of the E2 Ub-conjugating enzyme, UBCH5A, on SLC7A11 levels in H522 cells. UBCH5A knockdown and SLC7A11 were assessed via Western blot analysis under reducing or nonreducing conditions (for SLC7A11). (F) GSH levels in H522 cells subjected to UBCH5A knockdown. Effect of overexpression of UBCH5B on SLC7A11 levels (G) or GSH content (H). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.