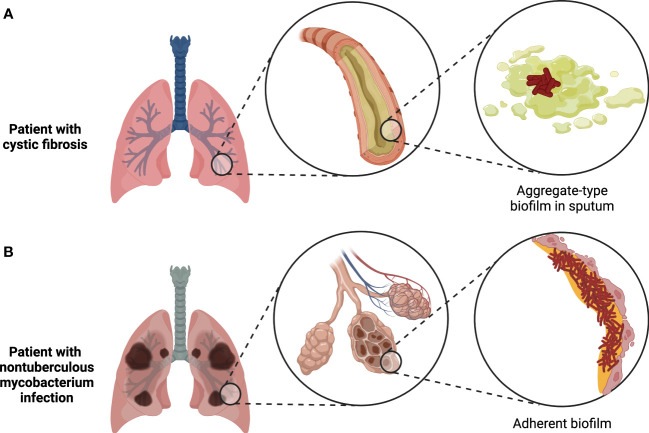
Figure 2.
Two major types of biofilms found in the human body. Tissue-associated biofilms generally either take the form of bacterial aggregates suspended in mucus or other host secretions, as in the case of biofilms found in cystic fibrosis patient sputum (A), or adherent biofilms attached to the surface of the tissue, as in the case of biofilms formed by nontuberculous mycobacteria during chronic infections (B). Figure created with BioRender.com.