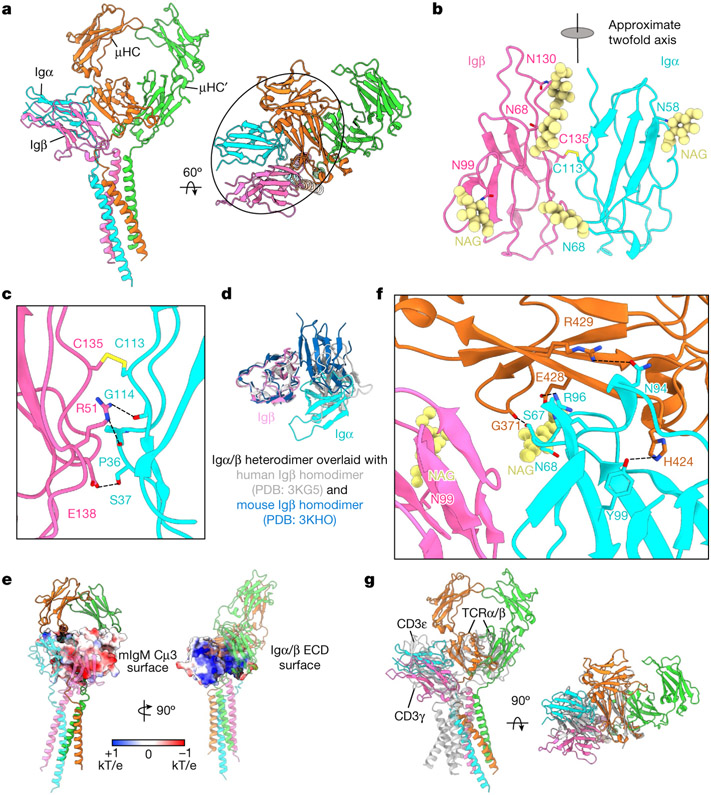
Fig. 2 ∣. ECD Interactions between the Igα/β heterodimer and mIgM.
a, Ribbon diagrams of the IgM BCRΔFab model in different views, with the ECD interactions circled. b, Ribbon diagram of the immunglobulin domains of the Igα/β heterodimer. The intersubunit disulfide bond between Igα C113 and Igβ C135 and the observed N-linked glycans are shown. The immunglobulin domains of Igα and Igβ are related by an approximate twofold axis. c, Detailed interfacial interactions between Igα and Igβ. d, Alignment of the immunglobulin domains of the Igα/β heterodimer with two different crystal structures of the Igβ homodimer, showing marked differences. e, Electrostatic surfaces (−1 to +1 kT/e) of the interacting Cμ4 (left) and the immunglobulin domains of the Igα/β heterodimer (right). f, Detailed interactions between ECD residues of the Igα/β heterodimer and the mIgM molecule. g, Alignment of the Cμ4 domain of IgM BCR with the TCRβ constant domain (grey), showing that the immunglobulin domains of the Igα/β and CD3ε–CD3γ (grey, PDB: 6JXR) heterodimers occupy the similar location relative to mIgM and TCRαβ, respectively.